High-Dose Intravenous Vitamin C Combined with Docetaxel in Men with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Phase II Trial
- PMID: 39076107
- PMCID: PMC11333993
- DOI: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-24-0225
High-Dose Intravenous Vitamin C Combined with Docetaxel in Men with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Phase II Trial
Abstract
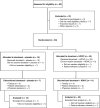
High-dose intravenous vitamin C (HDIVC) administered to produce pharmacologic concentrations shows promise in preclinical models and small clinical trials, but larger prospective randomized trials are lacking. We evaluated the clinical benefit of combining HDIVC with docetaxel in patients with progressive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). In this double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II trial, 47 patients were randomized 2:1 to receive docetaxel (75 mg/m2 i.v.) with either HDIVC (1 g/kg) or placebo. Coprimary endpoints were PSA50 response and adverse event rates. Secondary endpoints included overall survival, radiographic progression-free survival, and quality of life measured using the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Prostate instrument. Correlative analyses included pharmacokinetics and oxidative stress markers. Eighty-nine percent of patients previously had three or more lines of therapy. The PSA50 response rate was 41% in the HDIVC group and 33% in the placebo group (P = 0.44), with comparable adverse event rates in both groups. There were no significant differences in Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Prostate scores. The median radiographic progression-free survival was not significantly different between the HDIVC and placebo groups, with durations of 10.1 and 10.0 months (HR, 1.35; 95% confidence interval, 0.66-2.75; P = 0.40), respectively. The median overall survival was 15.2 months in the HDIVC group and 29.5 months in the placebo group (HR, 1.98; 95% confidence interval, 0.85-4.58; P = 0.11). HDIVC did not decrease F2-isoprostanes, indicators of oxidative stress. The study was suspended after prespecified interim analysis indicated futility in achieving primary endpoints. In this patient population, combining HDIVC with docetaxel did not improve PSA response, toxicity, or other clinical outcomes compared with docetaxel alone. Findings do not support the routine use of HDIVC in mCRPC treatment outside of clinical trials.
Significance: This is the first randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial to evaluate HDIVC in cancer treatment. The addition of HDIVC to docetaxel in patients with mCRPC does not improve PSA response, toxicity, or other clinical outcomes compared with docetaxel alone. The routine use of HDIVC in mCRPC treatment is not supported outside of clinical trials.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02516670.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
C.J. Paller reports grants from Bernie and Billi Marcus Foundation and DOD/NIH CDMRP during the conduct of the study, as well as personal fees from Bayer and Janssen, other support from AstraZeneca, grants and other support from Eli Lilly and Company, and grants from Merck outside the submitted work. E. Heath reports other support from Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, EMD Serono, Novartis, Sanofi, Janssen, Caris, Seattle Genetics, Arvinas, BioXcel, Bristol Myers Squibb, Calibr, Calithera, Corcept, Corvis, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Exelixis, Five Prime, Fortis, GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead Sciences, Harpoon, Hoffman-La Roche, Infinity, iTeos, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Merck, Mirati, Modra, Novartis, Oncolys, Peloton, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics, POINT Biopharma, and Seattle Genetics outside the submitted work. W.K. Kelly reports other support from Bayer, Janssen, and Amgen outside the submitted work. C. Hoimes reports grants, personal fees, and other support from Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb, Astellas, and Pfizer during the conduct of the study. P. Barata reports grants and personal fees from AVEO Oncology, Exelixis, AstraZeneca, and Janssen and personal fees from Pfizer, Caris Life Sciences, UroToday, Myovant, Merck, Targeted Oncology, Bristol Myers Squibb, MJH Life Sciences, Seagen, Eisai, and Astellas outside the submitted work. D.A. Garrison reports grants from Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine during the conduct of the study. C.H. Marshall reports personal fees from Tempus and grants from NIH/NCI, V Foundation, Prostate Cancer Foundation, and AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. E.S. Antonarakis reports grants and personal fees from Janssen, Sanofi, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Curium, Merck, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Clovis, and MacroGenics, personal fees from Aadi, Alkido, Astellas, Amgen, Blue Earth, Corcept, Exact Sciences, Hookipa, Invitae, Eli Lilly and Company, Foundation Medicine, Menarini Silicon Biosystems, Tango, Tempus, and Z-alpha, and grants from Novartis and Orion outside the submitted work, as well as a patent for an AR-V7 Biomarker Technology issued and licensed. M.A. Carducci reports grants from Marcus Foundation during the conduct of the study. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

