Value of Speckle Tracking Echocardiography Combined with Stress Echocardiography in Predicting Surgical Outcome of Severe Aortic Regurgitation with Markedly Reduced Left Ventricular Function
- PMID: 39076263
- PMCID: PMC11273019
- DOI: 10.31083/j.rcm2404114
Value of Speckle Tracking Echocardiography Combined with Stress Echocardiography in Predicting Surgical Outcome of Severe Aortic Regurgitation with Markedly Reduced Left Ventricular Function
Abstract
Background: Predicting outcomes of surgical aortic valve replacement (AVR) in patients with chronic severe aortic regurgitation (AR) and markedly reduced left ventricular (LV) function remains a challenge. This study aimed to explore the preoperative echocardiographic index that could predict the recovery of LV systolic function after surgery in patients with chronic severe AR and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF).
Methods: The study group consisted of 50 patients diagnosed with chronic severe AR ( 6 months) and significantly reduced LVEF (18~35%, average 26.2 5.3%). Low-dose dobutamine stress echocardiography (DSE) was performed before surgery. Only patients with an absolute increase in LVEF 8% during DSE were referred for surgical AVR. During following up (over six months to one year after surgery), the patients were divided into two groups by postoperative LVEF ( or 40%). DSE- and speckle tracking echocardiography (STE)-derived LV functional parameters were compared between groups to identify predictors of post-operative improvement in LVEF.
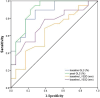
Results: A total of 38 patients underwent AVR. One patient died before discharge. Post-surgical LV size and LVEF improved markedly after surgery in all patients (n = 37). Pre-surgical LV end-systolic diameter, baseline global longitudinal strain (GLS) and peak GLS were better in the group with LVEF 40% (n = 18; p 0.05, t test). Baseline GLS and peak GLS correlated moderately with post-surgery LVEF (R = -0.581, p 0.001; R = -0.596, p 0.001; respectively). Logistic regression analysis demonstrated baseline GLS and peak GLS were the independent predictors of post-surgery improvement of LVEF. Peak GLS had the highest prediction value (area under the curve = 0.895, sensitivity and specificity: 89.5% and 77.8%, respectively), with a cutoff value of -9.4%.
Conclusions: This study shows that STE combined with DSE can provide sensitive quantitative indices for predicting improvement of LV systolic function after AVR in patients with chronic severe AR and significantly decreased LVEF.
Keywords: LVEF; aortic regurgitation; left ventricular systolic function; longitudinal strain; speckle tracking echocardiography; stress echocardiography.
Copyright: © 2023 The Author(s). Published by IMR Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Dujardin KS, Enriquez-Sarano M, Schaff HV, Bailey KR, Seward JB, Tajik AJ. Mortality and morbidity of aortic regurgitation in clinical practice. A long-term follow-up study. Circulation . 1999;99:1851–1857. - PubMed
-
- Fiedler AG, Bhambhani V, Laikhter E, Picard MH, Wasfy MM, Tolis G, et al. Aortic valve replacement associated with survival in severe regurgitation and low ejection fraction. Heart . 2018;104:835–840. - PubMed
-
- Chaliki HP, Mohty D, Avierinos JF, Scott CG, Schaff HV, Tajik AJ, et al. Outcomes after aortic valve replacement in patients with severe aortic regurgitation and markedly reduced left ventricular function. Circulation . 2002;106:2687–2693. - PubMed
-
- Kamath AR, Varadarajan P, Turk R, Sampat U, Patel R, Khandhar S, et al. Survival in patients with severe aortic regurgitation and severe left ventricular dysfunction is improved by aortic valve replacement: results from a cohort of 166 patients with an ejection fraction < or =35% Circulation . 2009;120:S134–S138. - PubMed
-
- Cho SH, Byun CS, Kim KW, Chang BC, Yoo KJ, Lee S. Preoperative indexed left ventricular dimensions to predict early recovery of left ventricular function after aortic valve replacement for chronic aortic regurgitation. Circulation Journal . 2010;74:2340–2345. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

