Polymer degrading marine Microbulbifer bacteria: an un(der)utilized source of chemical and biocatalytic novelty
- PMID: 39076296
- PMCID: PMC11285056
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.20.146
Polymer degrading marine Microbulbifer bacteria: an un(der)utilized source of chemical and biocatalytic novelty
Abstract
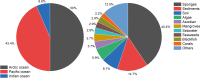
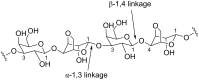
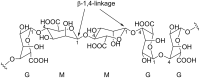
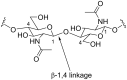
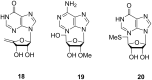
Microbulbifer is a genus of halophilic bacteria that are commonly detected in the commensal marine microbiomes. These bacteria have been recognized for their ability to degrade polysaccharides and other polymeric materials. Increasingly, Microbulbifer genomes indicate these bacteria to be an untapped reservoir for novel natural product discovery and biosynthetic novelty. In this review, we summarize the distribution of Microbulbifer bacteria, activities of the various polymer degrading enzymes that these bacteria produce, and an up-to-date summary of the natural products that have been isolated from Microbulbifer strains. We argue that these bacteria have been hiding in plain sight, and contemporary efforts into their genome and metabolome mining are going to lead to a proliferation of Microbulbifer-derived natural products in the future. We also describe, where possible, the ecological interactions of these bacteria in marine microbiomes.
Keywords: bacteria; hydrolases; marine natural products.
Copyright © 2024, Zhong and Agarwal.
Figures
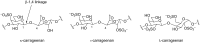
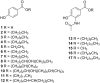
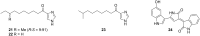
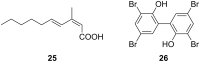



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
