The emerging role of oxidative stress in inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 39076514
- PMCID: PMC11284038
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1390351
The emerging role of oxidative stress in inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
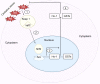
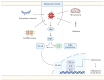
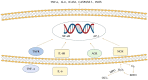
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic immune-mediated condition that affects the digestive system and includes Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). Although the exact etiology of IBD remains uncertain, dysfunctional immunoregulation of the gut is believed to be the main culprit. Amongst the immunoregulatory factors, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), components of the oxidative stress event, are produced at abnormally high levels in IBD. Their destructive effects may contribute to the disease's initiation and propagation, as they damage the gut lining and activate inflammatory signaling pathways, further exacerbating the inflammation. Oxidative stress markers, such as malondialdehyde (MDA), 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), and serum-free thiols (R-SH), can be measured in the blood and stool of patients with IBD. These markers are elevated in patients with IBD, and their levels correlate with the severity of the disease. Thus, oxidative stress markers can be used not only in IBD diagnosis but also in monitoring the response to treatment. It can also be targeted in IBD treatment through the use of antioxidants, including vitamin C, vitamin E, glutathione, and N-acetylcysteine. In this review, we summarize the role of oxidative stress in the pathophysiology of IBD, its diagnostic targets, and the potential application of antioxidant therapies to manage and treat IBD.
Keywords: IBD treatment; antioxidant therapy; inflammatory bowel disease; oxidative stress; oxidative stress markers.
Copyright © 2024 Muro, Zhang, Li, Zhao, Jin, Mao and Mao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

