Obstructive Shock, from Diagnosis to Treatment
- PMID: 39076909
- PMCID: PMC11266805
- DOI: 10.31083/j.rcm2307248
Obstructive Shock, from Diagnosis to Treatment
Abstract
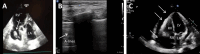
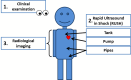
Shock is a life threatening pathological condition characterized by inadequate tissue oxygen supply. Four different subgroups of shock have been proposed according to the mechanism causing the shock. Of these, obstructive shock is characterized by reduction in cardiac output due to noncardiac diseases. The most recognized causes include pulmonary embolism, tension pneumothorax, pericardial tamponade and aortic dissection. Since obstructive shock typically cannot be stabilized unless cause for shock is resolved, diagnosis of the underlying disease is eminent. In this review, we therefore focus on diagnosis of obstructive shock and suggest a structured approach in three steps including clinical examination, ultrasound examination using the rapid ultrasound in shock (RUSH) protocol and radiological imaging if needed.
Keywords: circulatory shock; obstructive shock; review.
Copyright: © 2022 The Author(s). Published by IMR Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Vincent JL, De Backer D. Circulatory Shock. New England Journal of Medicine . 2013;369:1726–1734. - PubMed
-
- Hinshaw LB, Cox BG. The Fundamental mechanisms of shock; proceedings of a symposium held in Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, October 1–2, 1971 . Plenum Press; New York: 1972.
-
- Kumar A, Parrillo JE. Shock: Classification, Pathophysiology, and Approach to Management. Critical Care Medicine . 2008:371–420.
-
- Adams HA, Baumann G, Gänsslen A, Janssens U, Knoefel W, Koch T, et al. Die Definitionen der Schockformen. Intensivmedizin Und Notfallmedizin . 2001;38:541–553. - PubMed
-
- Astiz ME. Pathophysiology and Classification of Shock States . Elsevier; Philadelphia, PA: 2005. p. 677.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

