Correlation between Lactate Dehydrogenase to Albumin Ratio and the Prognosis of Patients with Cardiac Arrest
- PMID: 39077353
- PMCID: PMC11263156
- DOI: 10.31083/j.rcm2502065
Correlation between Lactate Dehydrogenase to Albumin Ratio and the Prognosis of Patients with Cardiac Arrest
Abstract
Background: Cardiac arrest (CA) is a common event in the intensive care unit (ICU), which seriously threatens the prognosis of patients. Therefore, it is crucial to determine a simple and effective clinical indicator to judge the prognosis of patients after a CA for later treatments. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between the lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio (LAR) and the prognosis of patients after a CA.
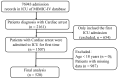
Methods: The clinical data of participants was obtained from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care IV (MIMIC-IV, v2.0; 2008 to 2019). According to the 30-day prognosis, patients were divided into a survivors group (n = 216) and a non-survivors group (n = 304). The optimal LAR threshold was determined using restricted cubic spline (RCS), which divided patients into a high LAR group ( 15.50, n = 257) and a low LAR group ( 15.50, n = 263). The ICU hospitalization and 30-day accumulative survival curves of the two groups were plotted following the Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. Multivariate Cox regression was used to analyze the relationship between the LAR and the prognosis of CA patients. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were drawn to evaluate the predictive efficacy of the LAR on 30-day all-cause mortality, and sensitivity analysis was used to check the reliability of the findings.
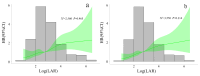
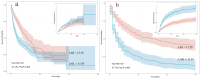
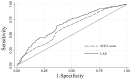
Results: A total of 520 patients with CA were enrolled and the 30-day mortality was 58.46%. The LAR in the non-survivors group was higher than in the survivors group. The RCS showed a linear trend relationship between the LAR and the mortality risk in patients during their ICU stay and 30 days; moreover, as the LAR increased, so did the risk of mortality. The Kaplan-Meier survival curve showed that compared with the low LAR group, the cumulative survival rates of ICU hospitalization and 30 days were lower in the high LAR group among CA patients (p 0.001). Multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that an elevated LAR ( 15.50) was an independent risk factor for mortality during ICU stay and 30 days (p 0.005). ROC analysis suggested that the LAR was superior to the sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score in predicting the 30-day all-cause mortality in CA patients (area under the curve (AUC) = 0.676, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.629-0.723). To verify the reliability of our findings, we performed sensitivity analyses and found that the findings were reliable.
Conclusions: An elevated LAR might be a predictor of mortality in patients following a CA during ICU hospitalization and 30 days, thereby it can be used to provide a reference for the clinical management of these patients.
Keywords: MIMIC-IV; cardiac arrest; clinical research; lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio; prognosis.
Copyright: © 2024 The Author(s). Published by IMR Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between lactate/albumin ratio and 28-day all-cause mortality in ischemic stroke patients without reperfusion therapy: a retrospective analysis of the MIMIC-IV database.Front Neurol. 2023 Oct 12;14:1271391. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1271391. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37900597 Free PMC article.
-
Association between lactate-to-albumin ratio and mortality in hepatic failure: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Mar 28;25(1):433. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10783-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40155840 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between initial red cell distribution width and ΔRDW and mortality in cardiac arrest patients.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Feb;11(1):433-443. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14602. Epub 2023 Nov 29. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 38030411 Free PMC article.
-
The correlation study between blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio and prognosis of patients with sepsis during hospitalization.BMC Anesthesiol. 2022 Dec 28;22(1):404. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01947-4. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022. PMID: 36577937 Free PMC article.
-
Lactate-to-Albumin Ratio (LAR) as a Predictor of All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2025 Apr 13;17(4):e82166. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82166. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40364881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Construction and validation of prognostic model for ICU mortality in cardiac arrest patients: an interpretable machine learning modeling approach.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Apr 24;30(1):328. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02588-2. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40275415 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio and 28-day mortality in septic patients with malignancies: analysis of the MIMIC-IV database.BMC Cancer. 2025 Apr 8;25(1):637. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14013-2. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40200294 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Lactic Dehydrogenase-to-Albumin Ratio and Short-Time Mortality in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025 Jul 15;20:2435-2444. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S521192. eCollection 2025. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025. PMID: 40688237 Free PMC article.
-
Lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio and prognosis in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 Apr 4;25(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03622-z. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40186178 Free PMC article.
-
Association between red blood cell distribution width to albumin ratio (RAR) and long-term prognosis of patients with sudden cardiac arrest.J Thorac Dis. 2025 May 30;17(5):3032-3052. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2024-2030. Epub 2025 May 28. J Thorac Dis. 2025. PMID: 40529766 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choi DS, Shin SD, Ro YS, Lee KW. Relationship between serum potassium level and survival outcome in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest using CAPTURES database of Korea: Does hypokalemia have good neurological outcomes in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine: Official Organ Wroclaw Medical University . 2020;29:727–734. - PubMed
-
- Jou C, Shah R, Figueroa A, Patel JK. The Role of Inflammatory Cytokines in Cardiac Arrest. Journal of Intensive Care Medicine . 2020;35:219–224. - PubMed
-
- Leloup M, Briatte I, Langlois A, Cariou A, Lesieur O, ACIR study group Unexpected cardiac arrests occurring inside the ICU: outcomes of a French prospective multicenter study. Intensive Care Medicine . 2020;46:1005–1015. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

