Current Perspectives on Atrial Amyloidosis: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 39077357
- PMCID: PMC11263142
- DOI: 10.31083/j.rcm2502073
Current Perspectives on Atrial Amyloidosis: A Narrative Review
Abstract
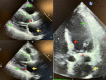
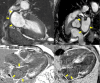
Amyloidosis is a systemic disease caused by low molecular weight protein accumulation in the extracellular space, which can lead to different degrees of damage, depending of the organ or tissue involved. The condition is defined cardiac amyloidosis (CA) when heart is affected, and it is associated with an unfavorable outcome. Different types of CA have been recognized, the most common (98%) are those associated with deposition of light chain (AL-CA), and the form secondary to transthyretin deposit. The latter can be classified into two types, a wild type (transthyretin amyloidosis wild type (ATTRwt)-CA), which mainly affects older adults, and the hereditary or variant type (ATTRh-CA or ATTRv-CA), which instead affects more often young people and is associated with genetic alterations. The atrial involvement can be isolated or linked to CA with a nonspecific clinical presentation represented by new onset atrial fibrillation (AF), diastolic dysfunction and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, or thromboembolism and stroke. Untreated patients have a median survival rate of 9 years for AL-CA and 7 years for ATTR-CA. By contrast, AL-CA and ATTR-CA treated patients have a median survival rate of 24 and 10 years, respectively. Atrial involvement in CA is a common but poor studied event, and alterations of performance can anticipate the anatomical damage. Recently, numerous advances have been made in the diagnostic field with improvements in the available techniques. An early diagnosis therefore allows a more effective therapeutic strategy with a positive impact on prognosis and mortality rate. A multimodality approach to the diagnosis of atrial involvement from CA is therefore recommended, and standard echocardiography, advanced Doppler-echocardiography (DE) and cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) can be useful to detect early signs of CA and to estabilish an appropriate treatment.
Keywords: amyloidosis; atrial; diagnosis; echocardiography; management.
Copyright: © 2024 The Author(s). Published by IMR Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

