Contribution of the Optical Coherence Tomography in Calcified Lesions
- PMID: 39077492
- PMCID: PMC11263993
- DOI: 10.31083/j.rcm2403093
Contribution of the Optical Coherence Tomography in Calcified Lesions
Abstract
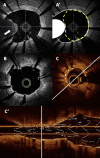
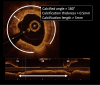
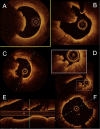
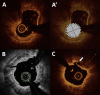
Coronary artery calcification is a complex process found predominantly in the elderly population. Coronary angiography frequently lacks sensitivity to detect, evaluate and quantify these lesions. Yet calcified lesions are considered stable, it remains associated with a higher rate of peri procedural complications during percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) including an increased risk of stent under expansion and struts mal apposition leading to poor clinical outcome. Intracoronary imaging (Intravascular Ultra Sound (IVUS) and Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)) allows better calcified lesions identification, localization within the coronary artery wall (superficial or deep calcifications), quantification. This lesions characterization allows a better choice of dedicated plaque-preparation tools (modified balloons, rotational or orbital atherectomy, intravascular lithotripsy) that are crucial to achieve optimal PCI results. OCT could also assess the impact of these tools on the calcified plaque morphology (plaque fracture, burring effects…). An OCT-guided tailored PCI strategy for calcified lesions still requires validation by clinical studies which are currently underway.
Keywords: coronary calcification; intravascular lithotripsy; optical coherence tomography; optical frequency domain imaging - rotational atherectomy; orbital atherectomy.
Copyright: © 2023 The Author(s). Published by IMR Press.
Conflict of interest statement
NC and BD declare no conflict of interest. PM declares consulting fees from Abbott Vascular and Terumo. GS declares consulting fees from Abbott Vascular and honoraria from Abbott Vascular and Terumo. NA declares grants from Abbott Vascular, consulting fees from Abbott Vascular and Boston Scientific and honoraria from Abbott Vascular and Boston Scientific.
Figures

References
-
- Madhavan MV, Tarigopula M, Mintz GS, Maehara A, Stone GW, Généreux P. Coronary artery calcification: pathogenesis and prognostic implications. Journal of the American College of Cardiology . 2014;63:1703–1714. - PubMed
-
- Mori H, Torii S, Kutyna M, Sakamoto A, Finn AV, Virmani R. Coronary Artery Calcification and its Progression: What Does it Really Mean? JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging . 2018;11:127–142. - PubMed
-
- Généreux P, Madhavan MV, Mintz GS, Maehara A, Palmerini T, Lasalle L, et al. Ischemic outcomes after coronary intervention of calcified vessels in acute coronary syndromes. Pooled analysis from the HORIZONS-AMI (Harmonizing Outcomes With Revascularization and Stents in Acute Myocardial Infarction) and ACUITY (Acute Catheterization and Urgent Intervention Triage Strategy) TRIALS. Journal of the American College of Cardiology . 2014;63:1845–1854. - PubMed
-
- Huisman J, van der Heijden LC, Kok MM, Danse PW, Jessurun GAJ, Stoel MG, et al. Impact of severe lesion calcification on clinical outcome of patients with stable angina, treated with newer generation permanent polymer-coated drug-eluting stents: A patient-level pooled analysis from TWENTE and DUTCH PEERS (TWENTE II) American Heart Journal . 2016;175:121–129. - PubMed
-
- Généreux P, Redfors B, Witzenbichler B, Arsenault MP, Weisz G, Stuckey TD, et al. Two-year outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention of calcified lesions with drug-eluting stents. International Journal of Cardiology . 2017;231:61–67. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

