The Challenge of Managing Atrial Fibrillation during Pregnancy
- PMID: 39077579
- PMCID: PMC11273119
- DOI: 10.31083/j.rcm2410279
The Challenge of Managing Atrial Fibrillation during Pregnancy
Abstract
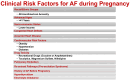
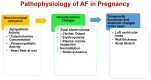
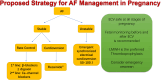
The incidence of atrial fibrillation (AF) during pregnancy increases with maternal age and with the presence of structural heart disorders. Early diagnosis and prompt therapy can considerably reduce the risk of thromboembolism. The therapeutic approach to AF during pregnancy is particularly challenging, and the maternal and fetal risks associated with the use of antiarrhythmic and anticoagulant drugs must be carefully evaluated. Moreover, the currently used thromboembolic risk scores have yet to be validated for the prediction of stroke during pregnancy. At present, electrical cardioversion is considered to be the safest and most effective strategy in women with hemodynamic instability. Beta-selective blockers are also recommended as the first choice for rate control. Antiarrhythmic drugs such as flecainide, propafenone and sotalol should be considered for rhythm control if atrioventricular nodal-blocking drugs fail. AF catheter ablation is currently not recommended during pregnancy. Overall, the therapeutic strategy for AF in pregnancy must be carefully assessed and should take into consideration the advantages and drawbacks of each aspect. A multidisciplinary approach with a "Pregnancy-Heart Team" appears to improve the management and outcome of these patients. However, further studies are needed to identify the most appropriate therapeutic strategies for AF in pregnancy.
Keywords: Pregnancy Heart Team; antiarrhythmic drugs (AADs); anticoagulants; atrial fibrillation (AF); electrical cardioversion (ECV); pregnancy.
Copyright: © 2023 The Author(s). Published by IMR Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Fabiana Lucà, Stefania Angela Di Fusco, and Furio Colivicchi are serving as Guest Editors of this journal; Alaide Chieffo is serving as one of the Editorial Board members of this journal. We declare that Fabiana Lucà, Stefania Angela Di Fusco, Furio Colivicchi, and Alaide Chieffo had no involvement in the peer review of this article and have no access to information regarding its peer review. Full responsibility for the editorial process for this article was delegated to Buddhadeb Dawn and Bernard Belhassen.
Figures

References
-
- Brundel BJJM, Ai X, Hills MT, Kuipers MF, Lip GYH, de Groot NMS. Atrial fibrillation. Nature Reviews: Disease Primers . 2022;8:21. - PubMed
-
- Tamirisa KP, Elkayam U, Briller JE, Mason PK, Pillarisetti J, Merchant FM, et al. Arrhythmias in Pregnancy. JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology . 2022;8:120–135. - PubMed
-
- Vaidya VR, Arora S, Patel N, Badheka AO, Patel N, Agnihotri K, et al. Burden of Arrhythmia in Pregnancy. Circulation . 2017;135:619–621. - PubMed
-
- Regitz-Zagrosek V, Roos-Hesselink JW, Bauersachs J, Blomström-Lundqvist C, Cífková R, De Bonis M, et al. 2018 ESC Guidelines for the management of cardiovascular diseases during pregnancy. European Heart Journal . 2018;39:3165–3241. - PubMed
-
- Greenwood JP, Scott EM, Stoker JB, Walker JJ, Mary DA. Sympathetic neural mechanisms in normal and hypertensive pregnancy in humans. Circulation . 2001;104:2200–2204. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

