Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of itepekimab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: Results from two terminated phase II trials
- PMID: 39077906
- PMCID: PMC11287337
- DOI: 10.1111/cts.13874
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of itepekimab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: Results from two terminated phase II trials
Erratum in
-
Correction to Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of itepekimab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: Results from two terminated phase II trials.Clin Transl Sci. 2024 Sep;17(9):e70026. doi: 10.1111/cts.70026. Clin Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39300731 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
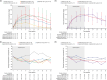
Interleukin-33 (IL-33) is a proinflammatory alarmin cytokine released by damaged epithelial tissue cells that initiates and amplifies both type 1 and type 2 inflammatory cascades. A role for IL-33 in atopic dermatitis (AD; a chronic, relapsing type 2 inflammatory disease of the skin) has been proposed. Itepekimab is a novel human IgG4P monoclonal antibody against IL-33, currently in clinical development for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Two global phase II studies-a dose-ranging itepekimab monotherapy study (NCT03738423) and a proof-of-concept study of itepekimab alone and in combination with dupilumab (NCT03736967)-were conducted in patients with moderate-to-severe AD to assess safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and efficacy; both studies were terminated following an interim analysis of the proof-of-concept study, which failed to demonstrate the efficacy of itepekimab. In these two studies, itepekimab exhibited linear and dose-proportional pharmacokinetics. Pharmacodynamics of total IL-33 indicated that itepekimab saturated binding to the target in serum at 300 mg q2w and q4w doses, and decreased blood eosinophil counts. Concentration-time profiles of itepekimab and total IL-33 were similar for itepekimab with or without dupilumab, and between East Asian and non-East Asian subgroups. Itepekimab was generally well tolerated, both alone and in combination with dupilumab. The lack of clinical efficacy for itepekimab observed in these studies suggests that IL-33 may not be a key pathogenic driver in moderate-to-severe AD.
© 2024 Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc and The Author(s). Clinical and Translational Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
M.P.K., M.A.K., E.A., J.D.D., and A.R. are employees and shareholders of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. X.Z., M.C.N., and A.S. are former employees and shareholders of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. E.G.‐Y. is a consultant for AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, AnaptysBio, Apogee Therapeutics, Apollo Therapeutics Ltd., Artax Biopharma Inc., AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelhiem, Cara Therapeutics, Centrexion Therapeutics Corporation, Connect Biopharma, Eli Lilly, Enveda Biosciences, Escient Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Fairmount Funds Management LLC, FL2022‐001, Inc., Galderma, Gate Bio, Google Ventures, GSK, Horizon Therapeutics USA, Inc., Incyte, Inmagene, Janssen, Japan Tobacco, Jasper Therapeutics, Kyowa Kirin, LEO Pharma, Merck, Nektar Therapeutics, Novartis, NUMAB Therapeutics AG, OrbiMed Advisors LLC, Pfizer, Pharmaxis Ltd, Pioneering Medicines VII, Inc., Proteologix US Inc., RAPT, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Ribon Therapeutics, Inc., Sanofi, SATO, Schrödinger, Inc., SPARC, Teva Branded Pharmaceutical Products R&D, Inc., UCB; and has received research funds from Amgen, AnaptysBio, Aslan, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cara Therapeutics, Concert, GSK, Incyte, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, LEO Pharma, Pfizer, RAPT, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Sanofi, UCB. M.J.C. has been an investigator for Atopix, Galapagos Pharmaceutical Company, Hyphens Pharma, Johnson & Johnson, Kymab, La Roche‐Posay, LEO Pharma, L'Oréal, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Sanofi; and is an advisory board member/consultant/speaker for Astellas, Atopix, Boots, Dermavant, Galapagos Pharmaceutical Company, Galderma, Hyphens Pharma, Johnson & Johnson, Kymab, La Roche‐Posay, LEO Pharma, L'Oréal, Menlo Therapeutics, Novartis, Oxagen, Pfizer, Procter & Gamble, Reckitt Benckiser, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Sanofi. M.W. reports honoraria and/or consulting fees from AbbVie, Aimmune Therapeutics, ALK‐Abelló, Allergopharma, Almirall, Amgen, Biotest, Boehringer Ingelheim, DBV Technologies, Genzyme, Kymab, LEO Pharma, Eli Lilly, Mylan, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Sanofi, Stallergenes Greer, Worg Pharmaceutics. D.‐H.N. declares no conflict of interest for this work. M.K.R. and S.H. are prior employees and shareholders of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. H.G. and C.R.X. are employees of Sanofi, and may hold stock and/or stock options in the company.
Figures

References
-
- Cayrol C, Girard JP. Interleukin‐33 (IL‐33): a nuclear cytokine from the IL‐1 family. Immunol Rev. 2018;281(1):154‐168. - PubMed
-
- Allinne J, Scott G, Lim WK, et al. IL‐33 blockade affects mediators of persistence and exacerbation in a model of chronic airway inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;144(6):1624‐1637.e10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

