New developments in Aspergillus fumigatus and host reactive oxygen species responses
- PMID: 39079399
- PMCID: PMC11475146
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2024.102521
New developments in Aspergillus fumigatus and host reactive oxygen species responses
Abstract
Aspergillus fumigatus is a filamentous fungus abundant in the environment and the most common causative agent of a spectrum of human diseases collectively termed aspergillosis. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis is caused by deficiencies in innate immune function that result in the inability of the host to clear inhaled Aspergillus conidia that then germinate and form invasive hyphae. Myeloid cells, and their ability to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), are essential for conidia clearance from the host. To combat ROS, A. fumigatus employs an expansive antioxidant system, though how these canonical antioxidant mechanisms contribute to infection initiation and disease progression remain to be fully defined. Recent research has identified noncanonical pathways in the A. fumigatus ROS response and new host populations with ROS deficiencies that are at-risk for invasive aspergillosis. Here, we highlight recent developments in the understanding of ROS at the interface of the dynamic A. fumigatus-host interaction.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
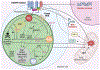
References
-
- GERSON SL: Prolonged Granulocytopenia: The Major Risk Factor for Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Patients with Acute Leukemia. Ann Intern Med 1984, 100:345. - PubMed
-
- Pollock JD, Williams DA, Gifford MAC, Li LL, Du X, Fisherman J, Orkin SH, Doerschuk CM, Dinauer MC: Mouse model of X–linked chronic granulomatous disease, an inherited defect in phagocyte superoxide production. Nat Genet 1995, 9:202–209. - PubMed
-
- Aratani Y, Kura F, Watanabe H, Akagawa H, Takano Y, Suzuki K, Dinauer MC, Maeda N, Koyama H: Relative contributions of myeloperoxidase and NADPH-oxidase to the early host defense against pulmonary infections with Candida albicans and Aspergillus fumigatus. Med Mycol 2002, 40:557–563. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

