Case-by-case combination of the prostate imaging reporting and data system version 2.1 with the Likert score to reduce the false-positives of prostate MRI: a proof-of-concept study
- PMID: 39079991
- PMCID: PMC11522071
- DOI: 10.1007/s00261-024-04506-2
Case-by-case combination of the prostate imaging reporting and data system version 2.1 with the Likert score to reduce the false-positives of prostate MRI: a proof-of-concept study
Abstract
Objectives: To retrospectively investigate whether a case-by-case combination of the Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System version 2.1 (PI-RADS) with the Likert score improves the diagnostic performance of mpMRI for clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa), especially by reducing false-positives.
Methods: One hundred men received mpMRI between January 2020 and April 2021, followed by prostate biopsy. Reader 1 (R1) and reader 2 (R2) (experience of > 3000 and < 200 mpMRI readings) independently reviewed mpMRIs with the PI-RADS version 2.1. After unveiling clinical information, they were free to add (or not) a Likert score to upgrade or downgrade or reinforce the level of suspicion of the PI-RADS category attributed to the index lesion or, rather, identify a new index lesion. We calculated sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values of R1/R2 in detecting csPCa when biopsying PI-RADS ≥ 3 index-lesions (strategy 1) versus PI-RADS ≥ 3 or Likert ≥ 3 index-lesions (strategy 2), with decision curve analysis to assess the net benefit. In strategy 2, the Likert score was considered dominant in determining biopsy decisions.
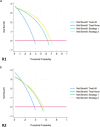
Results: csPCa prevalence was 38%. R1/R2 used combined PI-RADS and Likert categorization in 28%/18% of examinations relying mainly on clinical features such as prostate specific antigen level and digital rectal examination than imaging findings. The specificity/positive predictive values were 66.1/63.1% for R1 (95%CI 52.9-77.6/54.5-70.9) and 50.0/51.6% (95%CI 37.0-63.0/35.5-72.4%) for R2 in the case of PI-RADS-based readings, and 74.2/69.2% for R1 (95%CI 61.5-84.5/59.4-77.5%) and 56.6/54.2% (95%CI 43.3-69.0/37.1-76.6%) for R2 in the case of combined PI-RADS/Likert readings. Sensitivity/negative predictive values were unaffected. Strategy 2 achieved greater net benefit as a trigger of biopsy for R1 only.
Conclusion: Case-by-case combination of the PI-RADS version 2.1 with Likert score translated into a mild but measurable impact in reducing the false-positives of PI-RADS categorization, though greater net benefit in reducing unnecessary biopsies was found in the experienced reader only.
Keywords: Biopsy; Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging; PI-RADS; Prostatic neoplasms.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Turkbey B, Rosenkrantz AB, Haider MA, Padhani AR, Villeirs G, Macura KJ, Tempany CM, Choyke PL, Cornud F, Margolis DJ, Thoeny HC, Verma S, Barentsz J, Weinreb JC (2019) Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2.1: 2019 Update of Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2. Eur Urol. 76(3):340-351. 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.02.033 - PubMed
-
- Bogner K, Engelhard K, Wuest W, Hamel S (2022) Prostate cancer in PI-RADS scores 1 and 2 version 2.1: a comparison to previous PI-RADS versions. Abdom Radiol (NY). 47(6):2187–2196. 10.1007/s00261-022-03444-1 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

