HMGA1 promotes the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by elevating TKT-mediated upregulation of pentose phosphate pathway
- PMID: 39080260
- PMCID: PMC11289123
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-06933-x
HMGA1 promotes the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by elevating TKT-mediated upregulation of pentose phosphate pathway
Abstract
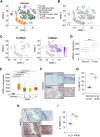
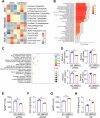
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) possesses a poor prognosis and treatment outcome. Dysregulated metabolism contributes to unrestricted growth of multiple cancers. However, abnormal metabolism, such as highly activated pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) in the progression of ESCC remains largely unknown. Herein, we report that high-mobility group AT-hook 1 (HMGA1), a structural transcriptional factor involved in chromatin remodeling, promoted the development of ESCC by upregulating the PPP. We found that HMGA1 was highly expressed in ESCC. Elevated HMGA1 promoted the malignant phenotype of ESCC cells. Conditional knockout of HMGA1 markedly reduced 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide (4NQO)-induced esophageal tumorigenesis in mice. Through the metabolomic analysis and the validation assay, we found that HMGA1 upregulated the non-oxidative PPP. With the transcriptome sequencing, we identified that HMGA1 upregulated the expression of transketolase (TKT), which catalyzes the reversible reaction in non-oxidative PPP to exchange metabolites with glycolytic pathway. HMGA1 knockdown suppressed the PPP by downregulating TKT, resulting in the reduction of nucleotides in ESCC cells. Overexpression of HMGA1 upregulated PPP and promoted the survival of ESCC cells by activating TKT. We further characterized that HMGA1 promoted the transcription of TKT by interacting with and enhancing the binding of transcription factor SP1 to the promoter of TKT. Therapeutics targeting TKT with an inhibitor, oxythiamine, reduced HMGA1-induced ESCC cell proliferation and tumor growth. Together, in this study, we identified a new role of HMGA1 in ESCCs by upregulating TKT-mediated activation of PPP. Our results provided a new insight into the role of HMGA1/TKT/PPP in ESCC tumorigenesis and targeted therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
High mobility group A1 (HMGA1) promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by inhibiting STING-mediated anti-tumor immunity.Nat Commun. 2025 Jun 2;16(1):5098. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60221-6. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40456764 Free PMC article.
-
Fra-1 Regulates the Expression of HMGA1, Which is Associated with a Poor Prognosis in Human Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Ann Surg Oncol. 2017 Oct;24(11):3446-3455. doi: 10.1245/s10434-016-5666-5. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27882471
-
HMGA1 drives chemoresistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing ferroptosis.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Feb 21;15(2):158. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06467-2. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38383528 Free PMC article.
-
High Mobility Group A1 Chromatin Keys: Unlocking the Genome During MPN Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 27;26(5):2125. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052125. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) in the glioma metabolism: A potent enhancer of malignancy.Biochimie. 2025 May;232:117-126. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2025.01.013. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Biochimie. 2025. PMID: 39894336 Review.
Cited by
-
NF-κB signaling is the major inflammatory pathway for inducing insulin resistance.3 Biotech. 2025 Feb;15(2):47. doi: 10.1007/s13205-024-04202-4. Epub 2025 Jan 20. 3 Biotech. 2025. PMID: 39845928
-
The Pentose Phosphate Pathway: From Mechanisms to Implications for Gastrointestinal Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 13;26(2):610. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020610. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STING inhibits the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing CPT1A-mediated fatty acid β-oxidation.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 May 20. doi: 10.1038/s41401-025-01581-z. Online ahead of print. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 40394235
-
STING exerts antiviral innate immune response by activating pentose phosphate pathway.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Dec 18;22(1):599. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01983-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39695767 Free PMC article.
-
High mobility group A1 (HMGA1) promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by inhibiting STING-mediated anti-tumor immunity.Nat Commun. 2025 Jun 2;16(1):5098. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60221-6. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40456764 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

