A machine learning model that outperforms conventional global subseasonal forecast models
- PMID: 39080287
- PMCID: PMC11289088
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-50714-1
A machine learning model that outperforms conventional global subseasonal forecast models
Abstract
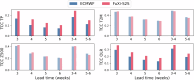
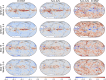
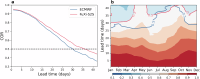
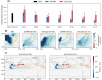
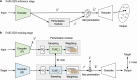
Skillful subseasonal forecasts are crucial for various sectors of society but pose a grand scientific challenge. Recently, machine learning-based weather forecasting models outperform the most successful numerical weather predictions generated by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), but have not yet surpassed conventional models at subseasonal timescales. This paper introduces FuXi Subseasonal-to-Seasonal (FuXi-S2S), a machine learning model that provides global daily mean forecasts up to 42 days, encompassing five upper-air atmospheric variables at 13 pressure levels and 11 surface variables. FuXi-S2S, trained on 72 years of daily statistics from ECMWF ERA5 reanalysis data, outperforms the ECMWF's state-of-the-art Subseasonal-to-Seasonal model in ensemble mean and ensemble forecasts for total precipitation and outgoing longwave radiation, notably enhancing global precipitation forecast. The improved performance of FuXi-S2S can be primarily attributed to its superior capability to capture forecast uncertainty and accurately predict the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO), extending the skillful MJO prediction from 30 days to 36 days. Moreover, FuXi-S2S not only captures realistic teleconnections associated with the MJO but also emerges as a valuable tool for discovering precursor signals, offering researchers insights and potentially establishing a new paradigm in Earth system science research.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- National Academies of Sciences. Next generation earth system prediction: strategies for subseasonal to seasonal forecasts (National Academies Press, Washington, DC, 2016).
-
- White, C. J. et al. Potential applications of subseasonal-to-seasonal (s2s) predictions. Meteorol Appl.24, 315–325 (2017).10.1002/met.1654 - DOI
-
- Pegion, K. et al. The subseasonal experiment (subx): a multimodel subseasonal prediction experiment. Bull. Am. Meteorol Soc.100, 2043–2060 (2019).10.1175/BAMS-D-18-0270.1 - DOI
-
- White, C. J. et al. Advances in the application and utility of subseasonal-to-seasonal predictions. Bull. Am. Meteorol Soc.103, E1448–E1472 (2022).10.1175/BAMS-D-20-0224.1 - DOI
-
- Domeisen, D. I. et al. Advances in the subseasonal prediction of extreme events: relevant case studies across the globe. Bull. Am. Meteorol Soc.103, E1473–E1501 (2022).10.1175/BAMS-D-20-0221.1 - DOI

