Dementia incidence varied by anticancer drugs and molecular targeted therapy in a population-based cohort study
- PMID: 39080315
- PMCID: PMC11289456
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-68199-9
Dementia incidence varied by anticancer drugs and molecular targeted therapy in a population-based cohort study
Abstract
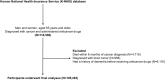
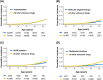
Anticancer drugs may affect the incidence of dementia by modulating the common pathophysiology between cancer and dementia. However, there is a paucity of research that focused on anticancer drugs with different mechanisms of action and their associations with subtypes of dementia. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the incidence of dementia according to various groups of anticancer drugs. From the Korea National Health Insurance Service database, our retrospective population-based cohort study enrolled 116,506 cancer patients aged 65 years and older who received anticancer drugs between January 1, 2008 and December 31, 2018. The hazard ratio was determined using Cox proportional hazards regression models, comparing each group of anticancer drugs to all other anticancer drugs, after adjusting for covariates. Antimetabolites (HR = 0.91; 95% CI 0.84-0.97) and molecular targeted therapies (HR = 0.60; 95% CI 0.49-0.74) were associated with a decreased incidence of dementia of the Alzheimer type (DAT), but not with vascular dementia. Among molecular targeted therapies, epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors (HR = 0.60; 95% CI 0.46-0.79) and multikinase inhibitors (HR = 0.49; 95% CI 0.27-0.89) were associated with a low incidence of DAT only. Our findings highlight the potential for targeted repurposing of anticancer drugs to prevent dementia.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Anticancer drug; Cancer; Dementia; Incidence; Vascular dementia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Increased risk of all-cause, Alzheimer's, and vascular dementia in adults with migraine in Korea: a population-based cohort study.J Headache Pain. 2022 Aug 24;23(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s10194-022-01484-y. J Headache Pain. 2022. PMID: 36002812 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of sleep apnea on alzheimer's disease in relation to sex: an 8-year longitudinal follow-up study of a nationwide cohort.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 Mar 20;17(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01667-6. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40114234 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term exposure to particulate matter and risk of Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia in Korea: a national population-based Cohort Study.Environ Health. 2023 Apr 14;22(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12940-023-00986-9. Environ Health. 2023. PMID: 37060077 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Atrial Fibrillation and the Risk of Dementia in the Korean Elderly: A 10-Year Nationwide Cohort Study.J Prev Med Public Health. 2020 Jan;53(1):56-63. doi: 10.3961/jpmph.19.117. Epub 2020 Jan 3. J Prev Med Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32023675 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of hypertension burden on subsequent dementia: a population-based cohort study.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 10;11(1):12291. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91923-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34112942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global action plan on the public health response to dementia 2017–2025. 44 p (World Health Organization, 2017).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

