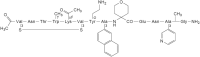
JNJ-77242113, a highly potent, selective peptide targeting the IL-23 receptor, provides robust IL-23 pathway inhibition upon oral dosing in rats and humans
- PMID: 39080319
- PMCID: PMC11289455
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-67371-5
JNJ-77242113, a highly potent, selective peptide targeting the IL-23 receptor, provides robust IL-23 pathway inhibition upon oral dosing in rats and humans
Abstract
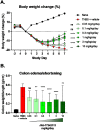
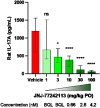
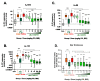
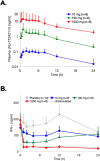
The interleukin (IL)-23 pathway is a pathogenic driver in psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease. Currently, no oral therapeutics selectively target this pathway. JNJ-77242113 is a peptide targeting the IL-23 receptor with high affinity (KD: 7.1 pM). In human cells, JNJ-77242113 potently and selectively inhibited proximal IL-23 signaling (IC50: 5.6 pM) without impacting IL-12 signaling. JNJ-77242113 inhibited IL-23-induced interferon (IFN)γ production in NK cells, and in blood from healthy donors and psoriasis patients (IC50: 18.4, 11 and 9 pM, respectively). In a rat trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis model, oral JNJ-77242113 attenuated disease parameters at doses ≥ 0.3 mg/kg/day. Pharmacologic activity beyond the gastrointestinal tract was also demonstrated. In blood from rats receiving oral JNJ-77242113, dose-dependent inhibition of ex vivo IL-23-stimulated IL-17A production was observed. In an IL-23-induced rat skin inflammation model, JNJ-77242113 inhibited IL-23-induced skin thickening and IL-17A, -17F and -22 gene induction. Oral dosing of JNJ-77242113 in healthy human volunteers inhibited ex vivo IL-23-stimulated IFNγ production in whole blood. Thus, JNJ-77242113 provided selective, systemic IL-23 pathway inhibition in preclinical models which translated to pharmacodynamic activity in healthy human volunteers, supporting the potential for JNJ-77242113 as a selective oral therapy for IL-23-driven immune-mediated diseases.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
AMF, LC, CG, BK, DP, AP, TB, RS, SJA, SS, MAR, AK, TK, and MCH are employees of Janssen Research & Development, LLC; employees may own stock/stock options in Johnson & Johnson, of which Janssen is a subsidiary. AB, SL, and NBM are employees of Protagonist Therapeutics, Inc and may own stock/stock options in the company. XC, DL, and KH were employees of Protagonist at the time these studies were conducted. XC is currently an employee of Anwita Biosciences and owns stock in Protagonist. KH is a Cytokinetics employee. XL, XX, RJP, CS, JPS and JT were employees of Janssen Research & Development, LLC, at the time these studies were conducted; XL is currently an employee of Takeda and JT is currently an employee of Vir Biotechnology.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

