Co-administration of xylo-oligosaccharides produced by immobilized Aspergillus terreus xylanase with carbimazole to mitigate its adverse effects on the adrenal gland
- PMID: 39080323
- PMCID: PMC11289116
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-67310-4
Co-administration of xylo-oligosaccharides produced by immobilized Aspergillus terreus xylanase with carbimazole to mitigate its adverse effects on the adrenal gland
Abstract
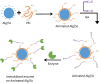
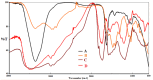
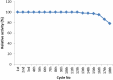
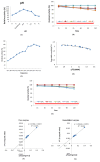
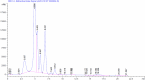
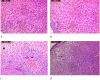
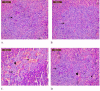
Carbimazole has disadvantages on different body organs, especially the thyroid gland and, rarely, the adrenal glands. Most studies have not suggested any solution or medication for ameliorating the noxious effects of drugs on the glands. Our study focused on the production of xylooligosaccharide (XOS), which, when coadministered with carbimazole, relieves the toxic effects of the drug on the adrenal glands. In addition to accelerating the regeneration of adrenal gland cells, XOS significantly decreases the oxidative stress caused by obesity. This XOS produced by Aspergillus terreus xylanase was covalently immobilized using microbial Scleroglucan gel beads, which improved the immobilization yield, efficiency, and operational stability. Over a wide pH range (6-7.5), the covalent immobilization of xylanase on scleroglucan increased xylanase activity compared to that of its free form. Additionally, the reaction temperature was increased to 65 °C. However, the immobilized enzyme demonstrated superior thermal stability, sustaining 80.22% of its original activity at 60 °C for 120 min. Additionally, the full activity of the immobilized enzyme was sustained after 12 consecutive cycles, and the activity reached 78.33% after 18 cycles. After 41 days of storage at 4 °C, the immobilized enzyme was still active at approximately 98%. The immobilized enzyme has the capability to produce xylo-oligosaccharides (XOSs). Subsequently, these XOSs can be coadministered alongside carbimazole to mitigate the adverse effects of the drug on the adrenal glands. In addition to accelerating the regeneration of adrenal gland cells, XOS significantly decreases the oxidative stress caused by obesity.
Keywords: Adrenal glands; Carbimazole drug; Covalent immobilization; Immobilized xylanase; Microbial scleroglucan; Xylo-oligosaccharides.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immobilization of xylanase from Bacillus pumilus strain MK001 and its application in production of xylo-oligosaccharides.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2007 Aug;142(2):125-38. doi: 10.1007/s12010-007-0013-8. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 18025574
-
Immobilization of xylanase on poly (ethylene glycol) methyl ether 5000 and its self-extractive bioconversion for the production of xylo-oligosaccharides.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014 Feb;172(4):2022-9. doi: 10.1007/s12010-013-0666-4. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24326682
-
Production of xylooligosaccharides by immobilized His-tagged recombinant xylanase from Penicillium occitanis on nickel-chelate Eupergit C.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014 Jul;173(6):1405-18. doi: 10.1007/s12010-014-0932-0. Epub 2014 May 7. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24801404
-
Enzymatic production of xylooligosaccharide from lignocellulosic and marine biomass: A review of current progress, challenges, and its applications in food sectors.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Oct;277(Pt 3):134014. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134014. Epub 2024 Jul 22. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39047995 Review.
-
Are phenolic compounds produced during the enzymatic production of prebiotic xylooligosaccharides (XOS) beneficial: a review.J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2024 Aug;26(8):867-882. doi: 10.1080/10286020.2024.2328723. Epub 2024 Apr 9. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2024. PMID: 38594834 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure of the Scleroglucan Biopolymer in Aqueous Solutions of Inorganic Salts and Ionic Liquids.ACS Omega. 2025 Jun 11;10(24):25884-25893. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c02212. eCollection 2025 Jun 24. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40584326 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

