Deciphering the role of protein kinase A in the control of FoxP3 expression in regulatory T cells in health and autoimmunity
- PMID: 39080325
- PMCID: PMC11289137
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-68098-z
Deciphering the role of protein kinase A in the control of FoxP3 expression in regulatory T cells in health and autoimmunity
Abstract
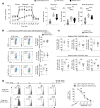
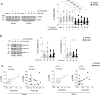
The molecular mechanisms that govern differential T cell development from CD4+CD25-conventional T (Tconv) into CD4+CD25+ forkhead-box-P3+ (FoxP3+) inducible regulatory T (iTreg) cells remain unclear. Herein, we investigated the relative contribution of protein kinase A (PKA) in this process. Mechanistically, we found that PKA controlled the efficiency of human iTreg cell generation through the expression of different FoxP3 splicing variants containing or not the exon 2. We found that transient PKA inhibition reduced the recruitment of cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) on regulatory regions of the FoxP3 gene, a condition that is associated with an impaired acquisition of their suppressive capacity in vitro. To corroborate our findings in a human model of autoimmunity, we measured CREB phosphorylation and FoxP3 levels in iTreg cells from treatment-naïve relapsing-remitting (RR)-multiple sclerosis (MS) subjects. Interestingly, both phospho-CREB and FoxP3 induction directly correlated and were significantly reduced in RR-MS patients, suggesting a previously unknown mechanism involved in the induction and function of human iTreg cells.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Compromised CD4+ CD25(high) regulatory T-cell function in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis is correlated with a reduced frequency of FOXP3-positive cells and reduced FOXP3 expression at the single-cell level.Immunology. 2008 Jan;123(1):79-89. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02690.x. Epub 2007 Sep 25. Immunology. 2008. PMID: 17897326 Free PMC article.
-
Glycolysis controls the induction of human regulatory T cells by modulating the expression of FOXP3 exon 2 splicing variants.Nat Immunol. 2015 Nov;16(11):1174-84. doi: 10.1038/ni.3269. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Nat Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26414764 Free PMC article.
-
Secondary progressive in contrast to relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients show a normal CD4+CD25+ regulatory T-cell function and FOXP3 expression.J Neurosci Res. 2006 Jun;83(8):1432-46. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20852. J Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16583400
-
Transcriptional regulation of Foxp3 in regulatory T cells.Immunobiology. 2011 Jun;216(6):678-85. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2010.11.002. Epub 2010 Nov 13. Immunobiology. 2011. PMID: 21122941 Review.
-
Regulatory T cells in autoimmune neuroinflammation.Immunol Rev. 2014 May;259(1):231-44. doi: 10.1111/imr.12169. Immunol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24712469 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

