Predicting hormone receptor status in invasive breast cancer through radiomics analysis of long-axis and short-axis ultrasound planes
- PMID: 39080346
- PMCID: PMC11289262
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-67145-z
Predicting hormone receptor status in invasive breast cancer through radiomics analysis of long-axis and short-axis ultrasound planes
Abstract
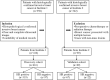
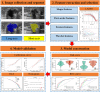
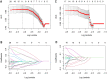
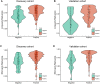
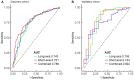
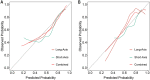
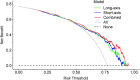
The hormone receptor (HR) status plays a significant role in breast cancer, serving as the primary guide for treatment decisions and closely correlating with prognosis. This study aims to investigate the predictive value of radiomics analysis in long-axis and short-axis ultrasound planes for distinguishing between HR-positive and HR-negative breast cancers. A cohort of 505 patients from two hospitals was stratified into discovery (Institute 1, 416 patients) and validation (Institute 2, 89 patients) cohorts. A comprehensive set of 788 ultrasound radiomics features was extracted from both long-axis and short-axis ultrasound planes, respectively. Utilizing least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression analysis, distinct models were constructed for the long-axis and short-axis data. Subsequently, radiomics scores (Rad-scores) were computed for each patient. Additionally, a combined model was formulated by integrating data from long-axis and short-axis Rad-scores along with clinical factors. The diagnostic efficacy of all models was evaluated by the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC). The long-axis and short-axis models, consisting of 11 features and 15 features, respectively, were established, yielding AUCs of 0.743 and 0.751 in the discovery cohort, and 0.795 and 0.744 in the validation cohort. The calculated long-axis and short-axis Rad-scores exhibited significant differences between HR-positive and HR-negative groups across all cohorts (all p < 0.001). Univariate analysis identified ultrasound-reported tumor size as an independent predictor. The combined model, incorporating long-axis and short-axis Rad-scores along with tumor size, achieved superior AUCs of 0.788 and 0.822 in the discovery and validation cohorts, respectively. The combined model effectively distinguishes between HR-positive and HR-negative breast cancers based on ultrasound radiomics features and tumor size, which may offer a valuable tool to facilitate treatment decision making and prognostic assessment.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Hormone receptor; Radiomics; Ultrasound.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integration of Longitudinal and Transverse Radiomics from Ultrasound Images with Clinical Factors for HER-2 Status Prediction in Invasive Breast Cancer Patients.J Invest Surg. 2024 Dec;37(1):2436050. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2024.2436050. Epub 2024 Dec 8. J Invest Surg. 2024. PMID: 39647167
-
[Preoperative prediction of HER-2 expression status in breast cancer based on MRI radiomics model].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2024 May 23;46(5):428-437. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20230816-00086. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38742356 Chinese.
-
Radiomics Analysis on Ultrasound for Prediction of Biologic Behavior in Breast Invasive Ductal Carcinoma.Clin Breast Cancer. 2018 Jun;18(3):e335-e344. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2017.08.002. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Clin Breast Cancer. 2018. PMID: 28890183
-
Prediction of Receptor Status in Radiomics: Recent Advances in Breast Cancer Research.Acad Radiol. 2024 Jul;31(7):3004-3014. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2023.12.012. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Acad Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38151383 Review.
-
Progress in research on ultrasound radiomics for predicting the prognosis of breast cancer.Cancer Innov. 2023 Jul 11;2(4):283-289. doi: 10.1002/cai2.85. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cancer Innov. 2023. PMID: 38089749 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hammond, M. E. et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med.134(6), 907–922. 10.5858/134.6.907 (2010). 10.5858/134.6.907 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

