Reliability of brain metrics derived from a Time-Domain Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy System
- PMID: 39080458
- PMCID: PMC11289386
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-68555-9
Reliability of brain metrics derived from a Time-Domain Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy System
Abstract
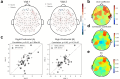
With the growing interest in establishing brain-based biomarkers for precision medicine, there is a need for noninvasive, scalable neuroimaging devices that yield valid and reliable metrics. Kernel's second-generation Flow2 Time-Domain Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (TD-fNIRS) system meets the requirements of noninvasive and scalable neuroimaging, and uses a validated modality to measure brain function. In this work, we investigate the test-retest reliability (TRR) of a set of metrics derived from the Flow2 recordings. We adopted a repeated-measures design with 49 healthy participants, and quantified TRR over multiple time points and different headsets-in different experimental conditions including a resting state, a sensory, and a cognitive task. Results demonstrated high reliability in resting state features including hemoglobin concentrations, head tissue light attenuation, amplitude of low frequency fluctuations, and functional connectivity. Additionally, passive auditory and Go/No-Go inhibitory control tasks each exhibited similar activation patterns across days. Notably, areas with the highest reliability were in auditory regions during the auditory task, and right prefrontal regions during the Go/No-Go task, consistent with prior literature. This study underscores the reliability of Flow2-derived metrics, supporting its potential to actualize the vision of using brain-based biomarkers for diagnosis, treatment selection and treatment monitoring of neuropsychiatric and neurocognitive disorders.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors were employed by Kernel during this study.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Speech-evoked activation in adult temporal cortex measured using functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS): Are the measurements reliable?Hear Res. 2016 Sep;339:142-54. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2016.07.007. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Hear Res. 2016. PMID: 27451015 Free PMC article.
-
Test-retest reliability of graph metrics in functional brain networks: a resting-state fNIRS study.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 9;8(9):e72425. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072425. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24039763 Free PMC article.
-
Test-retest assessment of independent component analysis-derived resting-state functional connectivity based on functional near-infrared spectroscopy.Neuroimage. 2011 Mar 15;55(2):607-15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.12.007. Epub 2010 Dec 10. Neuroimage. 2011. PMID: 21146616
-
Resting-state functional brain connectivity: lessons from functional near-infrared spectroscopy.Neuroscientist. 2014 Apr;20(2):173-88. doi: 10.1177/1073858413502707. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Neuroscientist. 2014. PMID: 24022325 Review.
-
Time domain functional NIRS imaging for human brain mapping.Neuroimage. 2014 Jan 15;85 Pt 1:28-50. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.106. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 23747285 Review.
Cited by
-
A compact time-domain diffuse optical tomography system for cortical neuroimaging.Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2025 Feb 20;3:imag_a_00475. doi: 10.1162/imag_a_00475. eCollection 2025. Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2025. PMID: 40800861 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

