Genetic insights into serum cathepsins as diagnostic and therapeutic targets in knee and hip osteoarthritis
- PMID: 39080459
- PMCID: PMC11289477
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-68718-8
Genetic insights into serum cathepsins as diagnostic and therapeutic targets in knee and hip osteoarthritis
Abstract
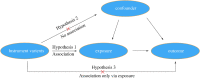
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a chronic disease due to the deterioration of cartilage structure and function, involving the progressive degradation of the cartilage extracellular matrix. Cathepsins, lysosomal cysteine proteases, play pivotal roles in various biological and pathological processes, particularly in protein degradation. Excess cathepsins levels are reported to contribute to the development of OA. However, the causal relationship between the cathepsin family and knee and hip OA remains uncertain. Therefore, this study utilized bidirectional Mendelian Randomization (MR) analyses to explore this causal association. Our results indicated that elevated serum levels of cathepsin O increase the overall risk of knee OA, while increased serum levels of cathepsin H enhance the risk of hip OA. Conversely, the reverse MR analyses did not reveal a reverse causal relationship between them. In summary, OA in different anatomical locations may genetically result from pathological elevations in different serum cathepsin isoforms, which could be utilized as diagnostic and therapeutic targets in clinical practice.
Keywords: Cathepsins; Extracellular matrix degradation; Hip osteoarthritis; Knee osteoarthritis; Mendelian randomization analyses.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Association of Biomarkers Such as CA, TP, TES and ALP With Osteoarthritis Risk: A Mendelian Randomized Study.Int J Rheum Dis. 2025 Jan;28(1):e70033. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.70033. Int J Rheum Dis. 2025. PMID: 39854182
-
Circulating cytokines levels and osteoarthritis: A Mendelian randomization study.Cytokine. 2024 Jul;179:156625. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2024.156625. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Cytokine. 2024. PMID: 38677184
-
Proteome-Wide Mendelian Randomization and Colocalization Analysis Identify Therapeutic Targets for Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 15;14(3):355. doi: 10.3390/biom14030355. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38540773 Free PMC article.
-
Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein, C-terminal cross-linking telopeptide of type II collagen, and matrix metalloproteinase-3 as biomarkers for knee and hip osteoarthritis (OA) diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 May;27(5):726-736. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2018.10.009. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019. PMID: 30391538
-
The Genetic Epidemiological Landscape of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: Where Are We Now and Where Are We Going?J Rheumatol. 2016 Feb;43(2):260-6. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.150710. Epub 2015 Dec 1. J Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26628593 Review.
Cited by
-
Revealing the causal relationship between cathepsin and inflammatory disease of wrist through Mendelian randomization.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Aug 1;104(31):e43461. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043461. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40760539 Free PMC article.
-
Causal relationship between cathepsins and major salivary gland neoplasms: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study.Gland Surg. 2024 Nov 30;13(11):2148-2162. doi: 10.21037/gs-24-374. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Gland Surg. 2024. PMID: 39678421 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

