Updates in chronic graft-versus-host disease: novel treatments and best practices in the current era
- PMID: 39080470
- PMCID: PMC11917373
- DOI: 10.1038/s41409-024-02370-8
Updates in chronic graft-versus-host disease: novel treatments and best practices in the current era
Abstract
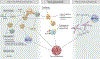
Chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) is a serious complication of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant. The development of cGVHD involves a complex, multistep process that is characterized by early inflammation and tissue injury, followed by chronic inflammation, aberrant tissue repair, and fibrosis. Systemic corticosteroids remain the first line of treatment for cGVHD. New treatments for patients with cGVHD for whom treatment has failed or who develop steroid-dependent cGVHD are now available; these include ibrutinib, ruxolitinib, and belumosudil. Treatment selection may be based on the patient's individual needs, graft-versus-host disease organ involvement, and comorbidities. However, as therapeutic options for patients without a treatment response or with only a partial response remain an unmet need, new agents are under investigation. Furthermore, patients with cGVHD can develop multiorgan involvement and frequently require specialized care. A multidisciplinary team approach that focuses on the individual's needs and quality of life is strongly encouraged.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
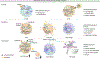
References
-
- Zeiser R, Blazar BR. Pathophysiology of chronic graft-versus-host disease and therapeutic targets. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(26):2565–2579. - PubMed
-
- Ratanatharathorn V, Nash RA, Przepiorka D, Devine SM, Klein JL, Weisdorf D, et al. Phase III study comparing methotrexate and tacrolimus (prograf, FK506) with methotrexate and cyclosporine for graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis after HLA-identical sibling bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1998;92(7):2303–2314. - PubMed
-
- Kröger N, Solano C, Wolschke C, Bandini G, Patriarca F, Pini M, et al. Antilymphocyte globulin for prevention of chronic graft-versus-host disease. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(1):43–53. - PubMed
-
- Bachier CR, Aggarwal SK, Hennegan K, Milgroom A, Francis K, Dehipawala S, et al. Epidemiology and treatment of chronic graft-versus-host disease post-allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a US claims analysis. Transplant Cell Ther. 2021;27(6):504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

