The uric acid/HDL-C ratio may predict significant coronary stenosis in moderate left main coronary artery lesions: an intravascular ultrasonography study
- PMID: 39080618
- PMCID: PMC11289968
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-024-02193-y
The uric acid/HDL-C ratio may predict significant coronary stenosis in moderate left main coronary artery lesions: an intravascular ultrasonography study
Erratum in
-
Correction: The uric acid/HDL-C ratio may predict significant coronary stenosis in moderate left main coronary artery lesions: an intravascular ultrasonography study.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Sep 3;23(1):281. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02251-5. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39227922 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: There may be severe difficulties in determining the severity of LMCA (left main coronary artery) lesions. The use of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) facilitates decisions about lesion severity in these patients. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between the UHR (uric acid to HDL-C ratio) and lesion severity in patients who underwent LMCA IVUS.
Methods: This study included 205 patients with ICS (intermediate coronary stenosis) in the LMCA who underwent IVUS. In the IVUS measurements of these patients, the plaque burden (PB) and the minimal lumen area (MLA) showing lesion severity were measured.
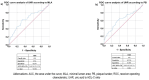
Results: The patients were separated into two groups according to plaque burden (< 65% and ≥ 65%). The UHR was significantly greater in the high plaque burden group (479.5 vs. 428.6, P = 0.001). When the patients were separated into two groups according to the MLA (< 6mm2 and ≥ 6mm2), the UHR was determined to be significantly greater in the group with low MLA (476.8 vs. 414.9, P < 0.001). In the ROC analysis performed according to the MLA and plaque burden values, the UHR cutoff value of 450 was found to have similar sensitivity and the same specificity for both parameters.
Conclusions: The results of this study suggested that there is a relationship between UHR and MLA < 6mm2 and plaque burden ≥ 65%, which are independently evaluated as critical in IVUS, and this could predict anatomically significant lesions in patients with a moderate degree of LMCA stricture.
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; Intravascular ultrasound; Left main coronary artery; Uric acid.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intravascular ultrasound-derived minimal lumen area criteria for functionally significant left main coronary artery stenosis.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014 Aug;7(8):868-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2014.02.015. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014. PMID: 25147031
-
Multimodality imaging of attenuated plaque using grayscale and virtual histology intravascular ultrasound and optical coherent tomography.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2016 Jul;88(1):E1-E11. doi: 10.1002/ccd.25786. Epub 2016 May 9. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2016. PMID: 25511369
-
Angiographically uncertain left main coronary artery narrowings: correlation with multidetector computed tomography and intravascular ultrasound.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2008 Jun;24(5):557-63. doi: 10.1007/s10554-007-9290-0. Epub 2007 Dec 30. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2008. PMID: 18165931
-
Diagnostic accuracy of intravascular ultrasound-derived minimal lumen area compared with fractional flow reserve--meta-analysis: pooled accuracy of IVUS luminal area versus FFR.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2014 Sep 1;84(3):377-85. doi: 10.1002/ccd.25047. Epub 2014 Apr 22. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2014. PMID: 23737441 Review.
-
Coronary CT angiography versus intravascular ultrasound for estimation of coronary stenosis and atherosclerotic plaque burden: a meta-analysis.J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2013 Jul-Aug;7(4):256-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2013.08.006. Epub 2013 Aug 23. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2013. PMID: 24148779 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between serum uric acid to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (UHR) and abdominal aortic calcification: a cross-sectional study based on NHANES 2013-2014.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 May 29;12:1560022. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1560022. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40510186 Free PMC article.
-
The potential of the serum uric acid to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio as a predictive biomarker of diabetes risk: a study based on NHANES 2005-2018.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 23;15:1499417. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1499417. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39916754 Free PMC article.
-
Association between uric acid to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and moderate-to-severe perivascular spaces burden: a retrospective cross-sectional study.Front Neurol. 2025 Aug 1;16:1609395. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1609395. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40823289 Free PMC article.
-
Correction: The uric acid/HDL-C ratio may predict significant coronary stenosis in moderate left main coronary artery lesions: an intravascular ultrasonography study.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Sep 3;23(1):281. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02251-5. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39227922 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Association of serum uric acid-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (UHR) with risk of myocardial infarction among individuals with diabetes: a cross-sectional analysis using data from NHANES 2005-2020.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jul 2;30(1):554. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02845-4. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40605038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the global burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;385(9963):117–71. 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

