Lenvatinib targets STAT-1 to enhance the M1 polarization of TAMs during hepatocellular carcinoma progression
- PMID: 39080642
- PMCID: PMC11289911
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-12680-1
Lenvatinib targets STAT-1 to enhance the M1 polarization of TAMs during hepatocellular carcinoma progression
Abstract
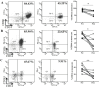
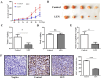
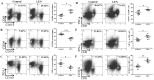
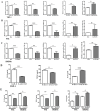
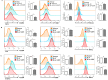
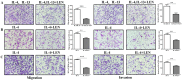
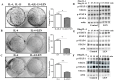
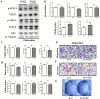
Lenvatinib, a multitarget kinase inhibitor, has been proven to be effective in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. It has been previously demonstrated that tumour associated macrophages (TAMs) in tumour tissues can promote HCC growth, invasion and metastasis. Furthermore, lenvatinib has certain immunomodulatory effects on the treatment of HCC. However, the role of lenvatinib in macrophage polarization during HCC treatment has not been fully explored. In this study, we used a variety of experimental methods both in vitro and in vivo to investigate the effect of lenvatinib on TAMs during HCC progression. This study is the first to show that lenvatinib can alter macrophage polarization in both humans and mice. Moreover, macrophages treated with lenvatinib in vitro displayed enhanced classically activated macrophages (M1) activity and suppressed liver cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and migration. Furthermore, during the progression of M1 macrophage polarization induced by lenvatinib, STAT-1 was the main target transcription factor, and inhibiting STAT-1 activity reversed the effect of lenvatinib. Overall, the present study provides a theoretical basis for the immunomodulatory function of lenvatinib in the treatment of HCC.
Keywords: HCC; Lenvatinib; STAT-1; TAMs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
β,β-Dimethylacrylalkannin, a Natural Naphthoquinone, Inhibits the Growth of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Modulating Tumor-Associated Macrophages.Molecules. 2024 Aug 20;29(16):3919. doi: 10.3390/molecules29163919. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39202998 Free PMC article.
-
STOML2 potentiates metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting PINK1-mediated mitophagy and regulates sensitivity to lenvatinib.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Jan 14;14(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-01029-3. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33446239 Free PMC article.
-
circCCNY enhances lenvatinib sensitivity and suppresses immune evasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by serving as a scaffold for SMURF1 mediated HSP60 degradation.Cancer Lett. 2025 Mar 1;612:217470. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217470. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Cancer Lett. 2025. PMID: 39826668
-
Lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma: From preclinical mechanisms to anti-cancer therapy.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020 Aug;1874(1):188391. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188391. Epub 2020 Jul 10. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32659252 Review.
-
Resistance of Lenvatinib in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2022;22(11):865-878. doi: 10.2174/1568009622666220428111327. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2022. PMID: 36267045 Review.
Cited by
-
Lenvatinib enhances antitumor immunity of anti-PD-1 antibody.Int J Clin Oncol. 2025 Apr;30(4):666-673. doi: 10.1007/s10147-025-02721-5. Epub 2025 Feb 22. Int J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39985645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of Tumor-Associated Macrophages to Overcome Immune Suppression in the Hepatocellular Carcinoma Microenvironment.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Dec 29;17(1):66. doi: 10.3390/cancers17010066. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39796695 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asafo-Agyei KO. H. Samant. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Treasure Island (FL); 2022.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ZR2023QH127, ZR2020QH177/Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation
- ZR2023QH127, ZR2020QH177/Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation
- 2019ZL002/Academic Promotion Program of Shandong First Medical University
- 2019RU071/Research Unit of Radiation Oncology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences
- 81627901, 81972863 and 82030082/the foundation of National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

