Lysine methylation modifications in tumor immunomodulation and immunotherapy: regulatory mechanisms and perspectives
- PMID: 39080807
- PMCID: PMC11289998
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-024-00621-w
Lysine methylation modifications in tumor immunomodulation and immunotherapy: regulatory mechanisms and perspectives
Abstract
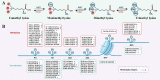
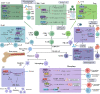
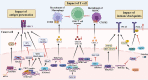
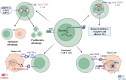
Lysine methylation is a crucial post-translational modification (PTM) that significantly impacts gene expression regulation. This modification not only influences cancer development directly but also has significant implications for the immune system. Lysine methylation modulates immune cell functions and shapes the anti-tumor immune response, highlighting its dual role in both tumor progression and immune regulation. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview of the intrinsic role of lysine methylation in the activation and function of immune cells, detailing how these modifications affect cellular processes and signaling pathways. We delve into the mechanisms by which lysine methylation contributes to tumor immune evasion, allowing cancer cells to escape immune surveillance and thrive. Furthermore, we discuss the therapeutic potential of targeting lysine methylation in cancer immunotherapy. Emerging strategies, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy, are being explored for their efficacy in modulating lysine methylation to enhance anti-tumor immune responses. By targeting these modifications, we can potentially improve the effectiveness of existing treatments and develop novel therapeutic approaches to combat cancer more effectively.
Keywords: Cancer immunotherapy; Epigenetic; Immunomodulation; Lysine demethylases (KDMs); Lysine methylation; Lysine methyltransferases (KMTs).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Roles of Lysine Methylation in Glucose and Lipid Metabolism: Functions, Regulatory Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Implications.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 19;14(7):862. doi: 10.3390/biom14070862. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting histone lysine methylation in cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Jun;150:1-22. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25578037 Review.
-
Histone lysine methylation dynamics: establishment, regulation, and biological impact.Mol Cell. 2012 Nov 30;48(4):491-507. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.11.006. Mol Cell. 2012. PMID: 23200123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone lysine-specific methyltransferases and demethylases in carcinogenesis: new targets for cancer therapy and prevention.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013 Jun;13(5):558-79. doi: 10.2174/1568009611313050007. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 23713993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tipping the lysine methylation balance in disease.Biopolymers. 2013 Feb;99(2):127-35. doi: 10.1002/bip.22136. Biopolymers. 2013. PMID: 23175387 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances on gene-related DNA methylation in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment: a clinical perspective.Clin Epigenetics. 2025 May 5;17(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s13148-025-01884-2. Clin Epigenetics. 2025. PMID: 40325471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: The emerging role of protein methylation/demethylation modification in disease and homeostasis.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Feb 10;12:1565598. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1565598. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 39995569 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hornbeck PV, Kornhauser JM, Tkachev S, Zhang B, Skrzypek E, Murray B, et al. PhosphoSitePlus: a comprehensive resource for investigating the structure and function of experimentally determined post-translational modifications in man and mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(Database issue):D261–70. 10.1093/nar/gkr1122 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

