Volumetric Semantic Instance Segmentation of the Plasma Membrane of HeLa Cells
- PMID: 39080881
- PMCID: PMC8321355
- DOI: 10.3390/jimaging7060093
Volumetric Semantic Instance Segmentation of the Plasma Membrane of HeLa Cells
Abstract
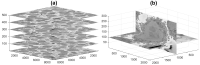
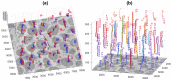
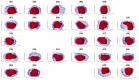
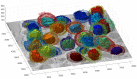
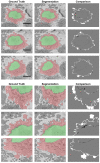
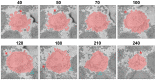
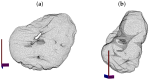
In this work, an unsupervised volumetric semantic instance segmentation of the plasma membrane of HeLa cells as observed with serial block face scanning electron microscopy is described. The resin background of the images was segmented at different slices of a 3D stack of 518 slices with 8192 × 8192 pixels each. The background was used to create a distance map, which helped identify and rank the cells by their size at each slice. The centroids of the cells detected at different slices were linked to identify them as a single cell that spanned a number of slices. A subset of these cells, i.e., the largest ones and those not close to the edges were selected for further processing. The selected cells were then automatically cropped to smaller regions of interest of 2000 × 2000 × 300 voxels that were treated as cell instances. Then, for each of these volumes, the nucleus was segmented, and the cell was separated from any neighbouring cells through a series of traditional image processing steps that followed the plasma membrane. The segmentation process was repeated for all the regions of interest previously selected. For one cell for which the ground truth was available, the algorithm provided excellent results in Accuracy (AC) and the Jaccard similarity Index (JI): nucleus: JI =0.9665, AC =0.9975, cell including nucleus JI =0.8711, AC =0.9655, cell excluding nucleus JI =0.8094, AC =0.9629. A limitation of the algorithm for the plasma membrane segmentation was the presence of background. In samples with tightly packed cells, this may not be available. When tested for these conditions, the segmentation of the nuclear envelope was still possible. All the code and data were released openly through GitHub, Zenodo and EMPIAR.
Keywords: HeLa cells; plasma membrane; semantic instance segmentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Impact of Training Data, Ground Truth and Shape Variability in the Deep Learning-Based Semantic Segmentation of HeLa Cells Observed with Electron Microscopy.J Imaging. 2023 Mar 1;9(3):59. doi: 10.3390/jimaging9030059. J Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36976110 Free PMC article.
-
Segmentation and Modelling of the Nuclear Envelope of HeLa Cells Imaged with Serial Block Face Scanning Electron Microscopy.J Imaging. 2019 Sep 12;5(9):75. doi: 10.3390/jimaging5090075. J Imaging. 2019. PMID: 34460669 Free PMC article.
-
Semantic segmentation of HeLa cells: An objective comparison between one traditional algorithm and four deep-learning architectures.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 2;15(10):e0230605. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230605. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33006963 Free PMC article.
-
Segmentation of white blood cells and comparison of cell morphology by linear and naïve Bayes classifiers.Biomed Eng Online. 2015 Jun 30;14:63. doi: 10.1186/s12938-015-0037-1. Biomed Eng Online. 2015. PMID: 26123131 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of automated segmentation of 3D computed-tomography scans for volumetric body composition analysis.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023 Oct;14(5):1973-1986. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13310. Epub 2023 Aug 10. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023. PMID: 37562946 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
How innovations in methodology offer new prospects for volume electron microscopy.J Microsc. 2022 Sep;287(3):114-137. doi: 10.1111/jmi.13134. Epub 2022 Jul 27. J Microsc. 2022. PMID: 35810393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Training Data, Ground Truth and Shape Variability in the Deep Learning-Based Semantic Segmentation of HeLa Cells Observed with Electron Microscopy.J Imaging. 2023 Mar 1;9(3):59. doi: 10.3390/jimaging9030059. J Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36976110 Free PMC article.
-
Online citizen science with the Zooniverse for analysis of biological volumetric data.Histochem Cell Biol. 2023 Sep;160(3):253-276. doi: 10.1007/s00418-023-02204-6. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Histochem Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37284846 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bich-Loan N.T., Kien K.T., Thanh N.L., Kim-Thanh N.T., Huy N.Q., The-Hai P., Muller M., Nachtergael A., Duez P., Thang N.D. Toxicity and Anti-Proliferative Properties of Anisomeles indica Ethanol Extract on Cervical Cancer HeLa Cells and Zebrafish Embryos. Life. 2021;11:257. doi: 10.3390/life11030257. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

