Diagnostic accuracy of galactomannan and lateral flow assay in invasive aspergillosis: A diagnostic meta-analysis
- PMID: 39082010
- PMCID: PMC11284428
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34569
Diagnostic accuracy of galactomannan and lateral flow assay in invasive aspergillosis: A diagnostic meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Efficient diagnosis of patients at high risk for invasive aspergillosis (IA) improves the outcome of the disease. Lateral flow assay (LFA) is a novel technology and assessing its diagnostic accuracy is of great significance in the clinical management of IA.
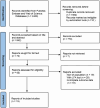
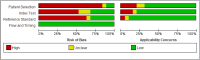
Methods: A meta-analysis using case-control studies was performed to assess the diagnostic performance of LFA alone or galactomannan (GM) combined with LFA (GM-LFA) as screening tests for IA. The sensitivity, specificity, and summary receiver operating characteristic curves were constructed.
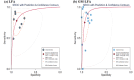
Results: Nineteen studies with 2838 patients were included. The pooled effect sizes for different indicators included: sensitivity (77 % for LFA and 75 % for GM-LFA), specificity (88 % for LFA and 87 % for GM-LFA), positive likelihood ratio (6.65 for LFA and 12.02 for GM-LFA), negative likelihood ratio (0.26 for LFA and 0.27 for GM-LFA), and the diagnostic odds ratio (25.81 for LFA and 44.87 for GM-LFA). The area under the curve was 0.91 for LFA and 0.94 for GM-LFA with a cut-off value ≥ 0.5.
Conclusion: The present meta-analysis suggested that LFA or GM-LFA at an optical density index (ODI) cutoff of ≥0.5 was a useful diagnostic tool for IA in patients. The results showed no significant differences in the accuracy of LFA alone and GM-LFA in diagnosing IA. In the clinical diagnosis and treatment of IA, LFA can be recommended if timely results are needed.
Keywords: Diagnostic meta-analysis; Galactomannan; Invasive aspergillosis; Lateral flow assay.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Diagnostic Efficacy of Aspergillus Galactomannan Lateral Flow Assay in Patients with Hematological Malignancies: A Prospective Multicenter Study.Mycopathologia. 2023 Oct;188(5):643-653. doi: 10.1007/s11046-023-00749-7. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Mycopathologia. 2023. PMID: 37273172 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Lateral Flow assay with digital reader for the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: A two-centre mixed cohort study.Mycoses. 2021 Oct;64(10):1197-1202. doi: 10.1111/myc.13352. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Mycoses. 2021. PMID: 34252244 Free PMC article.
-
Serum galactomannan for diagnosing invasive aspergillosis in pediatric patients: A meta-analysis.Microb Pathog. 2018 May;118:347-356. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.03.059. Epub 2018 Mar 31. Microb Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29614368
-
Comparative analysis of galactomannan lateral flow assay, galactomannan enzyme immunoassay and BAL culture for diagnosis of COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis.Mycoses. 2022 Oct;65(10):960-968. doi: 10.1111/myc.13518. Epub 2022 Aug 25. Mycoses. 2022. PMID: 35979737 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid galactomannan assay for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in adults: A meta-analysis.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022 Dec;47(12):1913-1922. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13792. Epub 2022 Nov 2. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022. PMID: 36324286 Review.
Cited by
-
Bronchoscopic Diagnosis of Severe Respiratory Infections.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 9;13(19):6020. doi: 10.3390/jcm13196020. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39408080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensitivity of serum galactomannan antigen in the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in patients with obstructive pulmonary diseases (asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases).Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2024 Nov 21;42(2):183-189. doi: 10.5114/ada.2024.145208. eCollection 2025 Apr. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2024. PMID: 40521067 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Approach to Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Hosts.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 9;14(2):389. doi: 10.3390/jcm14020389. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39860395 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kontoyiannis D.P., et al. Prospective surveillance for invasive fungal infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients, 2001-2006: overview of the Transplant-Associated Infection Surveillance Network (TRANSNET) Database. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010;50(8):1091–1100. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

