Validation of the NULL-EASE Score for Predicting Survival in a Multiethnic Asian Cohort of Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest
- PMID: 39082401
- PMCID: PMC11963946
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.123.034133
Validation of the NULL-EASE Score for Predicting Survival in a Multiethnic Asian Cohort of Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest
Abstract
Background: NULL-PLEASE is a simple and accurate clinical scoring system developed in a Western cohort of patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA). The need for blood test results limits its use in early stages of care. We adapted and validated the NULL-EASE score (without laboratory tests) in an independent, multiethnic Asian cohort of patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
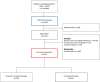
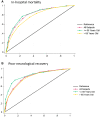
Methods and results: Using the Singapore OHCA registry, we included consecutive adult patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest who survived to hospital admission between April 2010 to December 2020. In-hospital mortality was the primary outcome. Logistic regression analyses were performed with STATA MP v18. Of 3274 patients (median age 64, interquartile range 54-75; 67.9% male) included in the study, 2476 (75.6%) had in-hospital mortality. NULL-EASE score was significantly lower in survivors compared with nonsurvivors (median [inter quartile range] 3 [1-4] versus 6 [4-7]; P<0.001) and strongly predictive of mortality (area under receiver operating characteristic, 0.81 [95% CI, 0.79-0.83]). Patients with a score of ≥3 had higher odds of mortality (adjusted odds ratio, 8.11 [95% CI, 6.57-10.00]) when compared with those with lower scores, after adjusting for sex, residential arrest, diabetes, respiratory disease, and stroke. A cutoff value of ≥3 predicted mortality with 92.2% sensitivity, 84.1% positive predictive value, 46.1% specificity, and 65.5% negative predictive value. NULL-EASE score performed better in younger compared with older patients (area under receiver operating characteristic, 0.82 versus 0.77, P=0.008).
Conclusions: The NULL-EASE score has good discriminative performance (sensitivity and accuracy) in our multiethnic Asian cohort, but the cutoff of ≥3 falls short of the desired level of specificity for therapeutic decision-making.
Keywords: cardiac arrest; prognosis; risk scores; survival.
Figures

References
-
- Panchal AR, Bartos JA, Cabañas JG, Donnino MW, Drennan IR, Hirsch KG, Kudenchuk PJ, Kurz MC, Lavonas EJ, Morley PT, et al. Part 3: adult basic and advanced life support: 2020 American Heart Association guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation. 2020;142:S366–S468. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000916 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nolan JP, Sandroni C, Böttiger BW, Cariou A, Cronberg T, Friberg H, Genbrugge C, Haywood K, Lilja G, Moulaert VRM, et al. European resuscitation council and European Society of Intensive Care Medicine guidelines 2021: post‐resuscitation care. Intensive Care Med. 2021;47:369–421. doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06368-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Neumar RW, Nolan JP, Adrie C, Aibiki M, Berg RA, Böttiger BW, Callaway C, Clark RS, Geocadin RG, Jauch EC, et al. Post‐cardiac arrest syndrome: epidemiology, pathophysiology, treatment, and prognostication. A consensus statement from the international liaison committee on resuscitation (American Heart Association, Australian and New Zealand council on resuscitation, European resuscitation council, Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, InterAmerican Heart Foundation, resuscitation Council of Asia, and the resuscitation Council of Southern Africa); the American Heart Association Emergency Cardiovascular Care Committee; the Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; the Council on Cardiopulmonary, Perioperative, and Critical Care; the Council on Clinical Cardiology; and the Stroke Council. Circulation. 2008;118:2452–2483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

