A randomised trial comparing 6-monthly adjuvant zoledronate with a single one-time dose in patients with early breast cancer
- PMID: 39083190
- PMCID: PMC11522049
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-024-07443-2
A randomised trial comparing 6-monthly adjuvant zoledronate with a single one-time dose in patients with early breast cancer
Abstract
Purpose: While adjuvant bisphosphonate use in early breast cancer (EBC) is associated with improvements in breast cancer-specific outcomes, questions remain around optimal bisphosphonate type, dose and scheduling. We evaluated a single zoledronate infusion in a prospective randomised trial.
Methods: Postmenopausal patients with EBC were randomised to receive a single infusion of zoledronate (4 mg IV) or 6-monthly treatment for 3 years. Outcomes measured were; Quality of Life (QoL; EQ-5D-5L), bisphosphonate-related toxicities, including acute phase reactions (APRs), recurrence-free survival (RFS), bone metastasis-free survival (BMFS) and overall survival (OS).
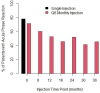
Results: 211 patients were randomized to either a single infusion (n = 107) or six-monthly treatment (n = 104). After 3 years of follow up there were no significant differences between the arms for QoL and most toxicity endpoints. APRs following zoledronate occurred in 81% (171/211) of patients (77.6% in single infusion arm and 84.6% in the 6-monthly group). While the frequency of APRs decreased over 3 years in the 6-monthly arm, they still remain common. Of 34/104 (32.7%) patients who discontinued zoledronate early in the 6-monthly treatment group, the most common reason was APRs (16/34, 47%). At the 3 year follow up, there were no differences between arms for RFS, BMFS or OS.
Conclusion: A single infusion of zoledronate was associated with increased patient convenience, less toxicity, and lower rates of treatment discontinuation. Despite the common clinical impression that APRs decrease with time, this was not observed when patients were specifically questioned. While the study is not powered for non-inferiority, longer-term follow-up for confirmation of RFS and OS rates is ongoing.
Keywords: Adjuvant; Bisphosphonates; Breast cancer; Zoledronate.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Clemons and Dhesy-Thind reported serving on the CCO-ASCO guideline committee. Conter reported being an employee of F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures
References
-
- Dhesy-Thind S, Fletcher GG, Blanchette PS et al (2017) Use of adjuvant bisphosphonates and other bone-modifying agents in breast cancer: a cancer care ontario and american society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol 35:2062–2081. 10.1200/JCO.2016.70.7257 - PubMed
-
- Hadji P, Coleman RE, Wilson C et al (2016) Adjuvant bisphosphonates in early breast cancer: consensus guidance for clinical practice from a European Panel. Ann Oncol 27:379–390. 10.1093/annonc/mdv617 - PubMed
-
- Gnant M, Mlineritsch B, Stoeger H et al (2011) Adjuvant endocrine therapy plus zoledronic acid in premenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer: 62-month follow-up from the ABCSG-12 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol 12:631–641. 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70122-X - PubMed
-
- Eisen A, Somerfield MR, Accordino MK et al (2022) Use of adjuvant bisphosphonates and other bone-modifying agents in breast cancer: ASCO-OH (CCO) guideline update. JCO 40:787–800. 10.1200/JCO.21.02647 - PubMed
-
- Eidtmann H, De Boer R, Bundred N et al (2010) Efficacy of zoledronic acid in postmenopausal women with early breast cancer receiving adjuvant letrozole: 36-month results of the ZO-FAST study. Ann Oncol 21:2188–2194. 10.1093/annonc/mdq217 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical