RNA variant assessment using transactivation and transdifferentiation
- PMID: 39084224
- PMCID: PMC11339655
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2024.06.018
RNA variant assessment using transactivation and transdifferentiation
Abstract
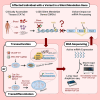
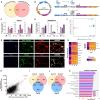
Understanding the impact of splicing and nonsense variants on RNA is crucial for the resolution of variant classification as well as their suitability for precision medicine interventions. This is primarily enabled through RNA studies involving transcriptomics followed by targeted assays using RNA isolated from clinically accessible tissues (CATs) such as blood or skin of affected individuals. Insufficient disease gene expression in CATs does however pose a major barrier to RNA based investigations, which we show is relevant to 1,436 Mendelian disease genes. We term these "silent" Mendelian genes (SMGs), the largest portion (36%) of which are associated with neurological disorders. We developed two approaches to induce SMG expression in human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs) to overcome this limitation, including CRISPR-activation-based gene transactivation and fibroblast-to-neuron transdifferentiation. Initial transactivation screens involving 40 SMGs stimulated our development of a highly multiplexed transactivation system culminating in the 6- to 90,000-fold induction of expression of 20/20 (100%) SMGs tested in HDFs. Transdifferentiation of HDFs directly to neurons led to expression of 193/516 (37.4%) of SMGs implicated in neurological disease. The magnitude and isoform diversity of SMG expression following either transactivation or transdifferentiation was comparable to clinically relevant tissues. We apply transdifferentiation and/or gene transactivation combined with short- and long-read RNA sequencing to investigate the impact that variants in USH2A, SCN1A, DMD, and PAK3 have on RNA using HDFs derived from affected individuals. Transactivation and transdifferentiation represent rapid, scalable functional genomic solutions to investigate variants impacting SMGs in the patient cell and genomic context.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests S.T.C. has no paid advisory roles to declare. S.T.C. is a volunteer member of ClinGen Expert Panels: Muscular Dystrophies and Myopathies GCEP and Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy VCEP. S.T.C. is named inventor of intellectual property (IP) relating to novel methods and biomarkers to identify DNA variants that alter pre-messenger RNA splicing: (1) PCT no. 2018904348 and (2) Australian Patent no. 2019379868. PCT no. 2019900836. This IP is unrelated to the data and outcomes described within this manuscript.
Figures






References
-
- Brnich S.E., Abou Tayoun A.N., Couch F.J., Cutting G.R., Greenblatt M.S., Heinen C.D., Kanavy D.M., Luo X., McNulty S.M., Starita L.M., et al. Recommendations for application of the functional evidence PS3/BS3 criterion using the ACMG/AMP sequence variant interpretation framework. Genome Med. 2019;12:3. doi: 10.1186/s13073-019-0690-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Richards S., Aziz N., Bale S., Bick D., Das S., Gastier-Foster J., Grody W.W., Hegde M., Lyon E., Spector E., et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015;17:405–424. doi: 10.1038/gim.2015.30. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

