Collapsing Glomerulopathy
- PMID: 39084754
- PMCID: PMC11296495
- DOI: 10.1053/j.akdh.2024.03.008
Collapsing Glomerulopathy
Abstract
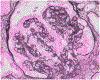
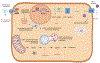
Collapsing glomerulopathy (CG) is a pattern of kidney injury characterized by segmental or global collapse of the glomerular tuft associated with overlying epithelial cell hyperplasia. Although CG may be idiopathic, a wide range of etiologies have been identified that can lead to this pattern of injury. Recent advances have highlighted the role of inflammatory and interferon signaling pathways and upregulation of apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1) within podocytes in those carrying a high-risk APOL1 genotype. In this review, we describe the etiology, pathogenesis, pathology, and clinical course of CG, focusing on nonviral etiologies. We also describe current treatments and explore potential therapeutic options targeting interferon/APOL1 pathways in CG.
Keywords: APOL1; Collapsing glomerulopathy; Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis; Interferon; Nephrotic syndrome; Podocyte.
Copyright © 2024 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Rao TK et al. Associated focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med 310, 669–673 (1984). - PubMed
-
- D’Agati VD, Fogo AB, Bruijn JA & Jennette JC Pathologic classification of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: a working proposal. Am. J. Kidney Dis 43, 368–382 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Barisoni L, Kriz W, Mundel P & D’Agati V The dysregulated podocyte phenotype: a novel concept in the pathogenesis of collapsing idiopathic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and HIV-associated nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 10, 51–61 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

