Histone serotonylation regulates ependymoma tumorigenesis
- PMID: 39085609
- PMCID: PMC11951423
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07751-z
Histone serotonylation regulates ependymoma tumorigenesis
Abstract
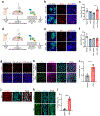
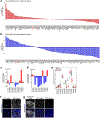
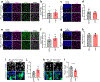
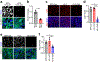
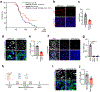
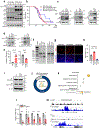
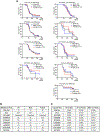
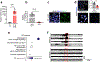
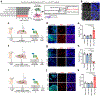
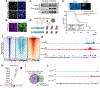
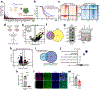
Bidirectional communication between tumours and neurons has emerged as a key facet of the tumour microenvironment that drives malignancy1,2. Another hallmark feature of cancer is epigenomic dysregulation, in which alterations in gene expression influence cell states and interactions with the tumour microenvironment3. Ependymoma (EPN) is a paediatric brain tumour that relies on epigenomic remodelling to engender malignancy4,5; however, how these epigenetic mechanisms intersect with extrinsic neuronal signalling during EPN tumour progression is unknown. Here we show that the activity of serotonergic neurons regulates EPN tumorigenesis, and that serotonin itself also serves as an activating modification on histones. We found that inhibiting histone serotonylation blocks EPN tumorigenesis and regulates the expression of a core set of developmental transcription factors. High-throughput, in vivo screening of these transcription factors revealed that ETV5 promotes EPN tumorigenesis and functions by enhancing repressive chromatin states. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is one of the genes repressed by ETV5, and its overexpression suppresses EPN tumour progression and tumour-associated network hyperactivity through synaptic remodelling. Collectively, this study identifies histone serotonylation as a key driver of EPN tumorigenesis, and also reveals how neuronal signalling, neuro-epigenomics and developmental programs are intertwined to drive malignancy in brain cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Figures
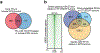

References
-
- Hanahan D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov 12, 31–46 (2022). - PubMed
Methods References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R35 NS132230/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA284455/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA223388/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL092332/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA217842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 23POST1019413/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- P30 CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS124093/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA243382/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA280203/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA281823/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD103555/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DC019668/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS116361/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

