Anti-infective immune functions of type IV interferon in grass carp ( Ctenopharyngodon idella): A novel antibacterial and antiviral interferon in lower vertebrates
- PMID: 39085753
- PMCID: PMC11491785
- DOI: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2024.008
Anti-infective immune functions of type IV interferon in grass carp ( Ctenopharyngodon idella): A novel antibacterial and antiviral interferon in lower vertebrates
Abstract
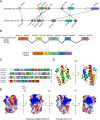
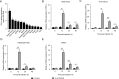
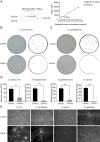
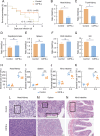
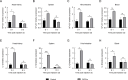
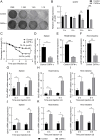
Type IV interferon (IFN-υ) is a recently discovered cytokine crucial for host defense against viral infections. However, the role and mechanisms of IFN-υ in bacterial infections remain unexplored. This study investigated the antibacterial and antiviral functions and mechanisms of grass carp ( Ctenopharyngodon idella) IFN-υ (CiIFN-υ) both in vivo and in vitro. The CiIFN-υ gene was first identified and characterized in grass carp. Subsequently, the immune expression of CiIFN-υ significantly increased following bacterial challenge, indicating its response to bacterial infections. The eukaryotic recombinant expression plasmid of CiIFN-υ was then constructed and transfected into fathead minnow (FHM) cells. Supernatants were collected and incubated with four bacterial strains, followed by plate spreading and colony counting. Results indicated that CiIFN-υ exhibited more potent antibacterial activity against gram-negative bacteria compared to gram-positive bacteria and aggregated gram-negative bacteria but not gram-positive bacteria. In vivo experiments further confirmed the antibacterial function, showing high survival rates, low tissue edema and damage, reduced tissue bacterial load, and elevated proinflammatory response at the early stages of bacterial infection. In addition, the antiviral function of CiIFN-υ was confirmed through in vitro and in vivo experiments, including crystal violet staining, survival rates, tissue viral burden, and RT-qPCR. This study highlights the antibacterial function and preliminary mechanism of IFN-υ, demonstrating that IFN-υ possesses dual functions against bacterial and viral infections.
IV型干扰素(IFN-υ)是最近发现的一种在宿主抵御病毒感染中起重要作用的细胞因子。IFN-υ在细菌感染中是否发挥重要作用,以及作用机制如何,目前仍不得而知。该研究探讨了草鱼IFN-υ(CiIFN-υ)在体内和体外的抗菌和抗病毒功能及机制。首先,对草鱼CiIFN-υ基因进行了鉴定和特征描述。CiIFN-υ表达水平在细菌感染后显著增加,表明CiIFN-υ对细菌感染有响应。接着,我们构建了CiIFN-υ的真核重组表达质粒,将其转染到FHM细胞中,收集上清液,将含有CiIFN-υ蛋白的上清液分别与四种菌株共孵育,涂布在LB培养板上并进行菌落计数等。结果表明,CiIFN-υ对革兰氏阴性菌比革兰氏阳性菌具有更强的抗菌活性,且能凝集革兰氏阴性菌,不能凝集革兰氏阳性菌。此外,体内实验也很好的验证了其抗菌功能,在细菌感染的早期阶段,促炎反应增强,随后组织水肿和组织损伤小,组织细菌载量少,存活率高。最后,通过细胞结晶紫染色、统计草鱼存活率、组织病毒载量和RT-qPCR等实验证实了CiIFN-υ的抗病毒功能。该研究强调了IFN-υ的抗菌功能和初步机制,研究结果表明草鱼的IFN-υ具有抗细菌和病毒感染的双重功能。.
Keywords: Antimicrobial immunity; Antiviral activity; Bactericidal activity; Grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella); IFN-υ.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
