Association between adherence to a lifestyle behavior and the risk of asthma in overweight and obese adolescents
- PMID: 39085812
- PMCID: PMC11293021
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-024-04967-w
Association between adherence to a lifestyle behavior and the risk of asthma in overweight and obese adolescents
Abstract
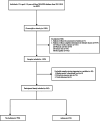
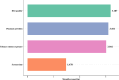
With the increasing prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents, to actively prevent the occurrence of asthma in this population is important for reducing the burden of the disease. Lifestyle factors, including diet and exercise, are importance for overweight and obese adolescents, as well as an important modifiable factor affecting airway inflammation and asthma, whether healthy lifestyle was correlated with the risk of asthma in adolescents ≥ 12 years has not been reported. We suspected that there might be correlation between healthy lifestyle behaviors and the risk of asthma in overweight and obese adolescents. This cross-sectional study aimed to explore the association between the adherence to a healthy lifestyle behaviors and the risk of asthma in overweight and obese adolescents based on the data of 945 participants aged between 12-18 years from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES). Univariable and multivariable weighted Logistic regression models were applied to evaluate the association between healthy lifestyle behaviors with asthma risk in overweight and obese adolescents. Odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were applied as estimates. We found that the risk of asthma was reduced in overweight and obese adolescents with intermediate (OR = 0.40, 95%CI: 0.17-0.94) or good lifestyle behaviors (OR = 0.33, 95%CI: 0.13-0.86) in comparison to those with poor lifestyle behaviors. In summary, intermediate or good lifestyle behaviors was correlated with decreased risk of asthma in overweight and obese adolescents, which might provide a reference for making further prevention strategies for asthma in adolescents.
Keywords: Adolescents; Asthma; Healthy lifestyle behaviors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical