Investigation of peripheral inflammatory biomarkers in association with violence in schizophrenia
- PMID: 39085826
- PMCID: PMC11293062
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-024-05966-y
Investigation of peripheral inflammatory biomarkers in association with violence in schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: Violent behavior carried out by patients with schizophrenia (SCZ) is a public health issue of increasing importance that may involve inflammation. Peripheral inflammatory biomarkers, such as the systemic immune inflammation index (SII), the neutrophil lymphocyte ratio (NLR), the platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and the monocyte lymphocyte ratio (MLR) are objective, easily accessible and cost-effective measures of inflammation. However, there are sparse studies investigating the role of peripheral inflammatory biomarkers in violence of patients with SCZ.
Methods: 160 inpatients diagnosed with SCZ between January and December 2022 were recruited into this study. Violent behavior and positive symptoms of all participants were evaluated using Modified Overt Aggression Scale (MOAS) and Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS), respectively. The partial correlation analysis was performed to examine the relationship of inflammatory indices and positive symptoms. Based on machine learning (ML) algorithms, these different inflammatory indices between groups were used to develop predictive models for violence in SCZ patients.
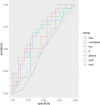
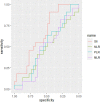
Results: After controlling for age, SII, NLR, MLR and PANSS positive scores were found to be increased in SCZ patients with violence, compared to patients without violence. SII, NLR and MLR were positively related to positive symptoms in all participants. Positive symptoms partially mediated the effects of peripheral inflammatory indices on violent behavior in SCZ. Among seven ML algorithms, penalized discriminant analysis (pda) had the best performance, with its an area under the receiver operator characteristic curve (AUC) being 0.7082. Subsequently, with the use of pda, we developed predictive models using four inflammatory indices, respectively. SII had the best performance and its AUC was 0.6613.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that inflammation is involved in violent behavior of SCZ patients and positive symptoms partially mediate this association. The models built by peripheral inflammatory indices have a good median performance in predicting violent behavior in SCZ patients.
Keywords: Inflammation; Schizophrenia; Violence.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

