Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000467 promotes colorectal cancer progression by promoting eIF4A3-mediated c-Myc translation
- PMID: 39085875
- PMCID: PMC11290134
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-024-02052-5
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000467 promotes colorectal cancer progression by promoting eIF4A3-mediated c-Myc translation
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second most common malignant tumor worldwide, and its incidence rate increases annually. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for improving the prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer. Circular RNAs are noncoding RNAs with a closed-loop structure that play a significant role in tumor development. However, the role of circular RNAs in CRC is poorly understood.
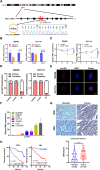
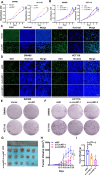
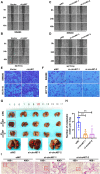
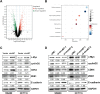
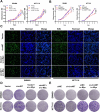
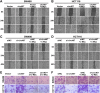
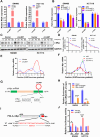
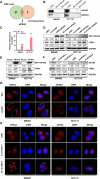
Methods: The circular RNA hsa_circ_0000467 was screened in CRC circRNA microarrays using a bioinformatics analysis, and the expression of hsa_circ_0000467 in CRC tissues was determined by in situ hybridization. The associations between the expression level of hsa_circ_0000467 and the clinical characteristics of CRC patients were evaluated. Then, the role of hsa_circ_0000467 in CRC growth and metastasis was assessed by CCK8 assay, EdU assay, plate colony formation assay, wound healing assay, and Transwell assay in vitro and in a mouse model of CRC in vivo. Proteomic analysis and western blotting were performed to investigate the effect of hsa_circ_0000467 on c-Myc signaling. Polysome profiling, RT‒qPCR and dual-luciferase reporter assays were performed to determine the effect of hsa_circ_0000467 on c-Myc translation. RNA pull-down, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) and immunofluorescence staining were performed to assess the effect of hsa_circ_0000467 on eIF4A3 distribution.
Results: In this study, we found that the circular RNA hsa_circ_0000467 is highly expressed in colorectal cancer and is significantly correlated with poor prognosis in CRC patients. In vitro and in vivo experiments revealed that hsa_circ_0000467 promotes the growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells. Mechanistically, hsa_circ_0000467 binds eIF4A3 to suppress its nuclear translocation. In addition, it can also act as a scaffold molecule that binds eIF4A3 and c-Myc mRNA to form complexes in the cytoplasm, thereby promoting the translation of c-Myc. In turn, c-Myc upregulates its downstream targets, including the cell cycle-related factors cyclin D2 and CDK4 and the tight junction-related factor ZEB1, and downregulates E-cadherin, which ultimately promotes the growth and metastasis of CRC.
Conclusions: Our findings revealed that hsa_circRNA_0000467 plays a role in the progression of CRC by promoting eIF4A3-mediated c-Myc translation. This study provides a theoretical basis and molecular target for the diagnosis and treatment of CRC.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Growth; Metastasis; Translation; c-Myc; eIF4A3; hsa_circRNA_0000467.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82203233/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023JJ60469/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- 2023RC3199/Science and technology innovation Program of Hunan Province
- 202203034978/Research Project of Health Commission of Hunan Province
- 2020TP1018/Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Department
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

