The triglyceride-glucose index is a predictor of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease and psoriasis: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 39085887
- PMCID: PMC11290256
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-024-01423-8
The triglyceride-glucose index is a predictor of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease and psoriasis: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: The association between the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index and clinical outcomes in patients with both coronary artery disease (CAD) and psoriasis is unclear. This study investigated the association between the TyG index and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with both CAD and psoriasis.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included patients diagnosed with both CAD and psoriasis who underwent coronary angiography at the Fuwai Hospital, Beijing, China, between January 2017 and May 2022. The study endpoint was the occurrence of MACE or end of follow-up time. Multivariate Cox proportional analysis and restricted cubic splines (RCS) were used to determine the association between the TyG index and MACE. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to determine the optimal threshold value of the TyG index for predicting MACE.
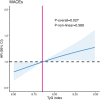
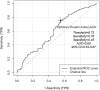
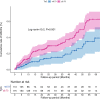
Results: This study enrolled 293 patients with both CAD and psoriasis, including 258 (88.1%) males with a mean age of 58.89 ± 9.61 years. Patients were divided into four groups based on the TyG quartiles: Q1 (N = 74), Q2 (N = 73), Q3 (N = 73), and Q4 (N = 73). After adjusting for the potential confounders, the TyG index was independently associated with MACE, both as a continuous variable (HR = 1.53, 95% CI = 1.03-2.28, P = 0.035) and as a categorical variable (Q1: reference; Q2: HR = 1.85, 95% CI = 0.88-3.87, P = 0.105; Q3: HR = 2.39, 95% CI = 1.14-5.00, P = 0.021; Q4: HR = 2.19, 95% CI = 1.001-4.81, P = 0.0497; P for trend = 0.039). RCS analysis showed an linear association between the TyG index and MACE (P-overall = 0.027, P-non-linear = 0.589). ROC curve analysis showed that the TyG index of ≥ 8.73 was the optimal threshold value (area under the ROC curve = 0.60, 95% CI 0.53-0.67). TyG index ≥ 8.73 was significantly associated with MACE (HR = 2.10, 95% CI = 1.32-3.34, P = 0.002). After adjustment for confounders, the TyG index showed independent association with MACE (HR = 2.00, 95% CI = 1.17-3.42, P = 0.011).
Conclusions: The TyG index showed a positive linear correlation with MACE in patients with both CAD and psoriasis. The TyG index of ≥ 8.73 might be the optimal threshold for predicting MACE.
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; MACE; Psoriasis; Triglyceride-glucose index.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The triglyceride-glucose index predicts 1-year major adverse cardiovascular events in end-stage renal disease patients with coronary artery disease.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Oct 27;22(1):292. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02028-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37891651 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of triglyceride-glucose index for the evaluation of coronary artery disease severity and occurrence of major adverse cardiovascular events.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2025 Jan 1;328(1):H14-H20. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00684.2024. Epub 2024 Nov 19. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39560964
-
Prognostic significance of the triglyceride-glucose index for patients with ischemic heart failure after percutaneous coronary intervention.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 6;14:1100399. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1100399. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36814584 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride-glucose index and coronary artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of risk, severity, and prognosis.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Jul 6;22(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01906-4. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37415168 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride-glucose index's link to cardiovascular outcomes post-percutaneous coronary intervention in China: a meta-analysis.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Jun;11(3):1317-1328. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14679. Epub 2024 Jan 21. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 38246749 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Associations of triglyceride glucose-body mass index with short-term mortality in critically ill patients with ischemic stroke.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Feb 28;24(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02583-1. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40022139 Free PMC article.
-
Does diabetes modify the triglyceride-glucose index associated with cardiovascular events and mortality? A meta-analysis of 50 cohorts involving 7,239,790 participants.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jan 27;24(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02585-z. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 39871273 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

