Blood pressure control in diabetic kidney disease: a post-hoc analysis of the FANTASTIC trial
- PMID: 39085979
- PMCID: PMC11293031
- DOI: 10.1186/s40885-024-00280-x
Blood pressure control in diabetic kidney disease: a post-hoc analysis of the FANTASTIC trial
Abstract
Background: The target blood pressure (BP) value is unclear for diabetic kidney disease (DKD). Therefore, we aimed to evaluate the effect of strict BP control or 'on treatment' BP on clinical outcomes in patients with DKD.
Methods: A post-hoc analysis of the prespecified secondary outcomes of the FimAsartaN proTeinuriA SusTaIned reduCtion in comparison with losartan in diabetic chronic kidney disease (FANTASTIC) trial, a randomized multicenter double-blind phase III trial. Eligible patients were aged ≥ 19 years with DKD. We assigned 341 participants with DKD to BP control strategy (standard-systolic BP [SBP] < 140 mmHg versus strict-SBP < 130 mmHg). The outcome was the occurrence of cardiovascular events and renal events. Separate analyses were performed to compared the risk of outcome according to achieved average BP levels.
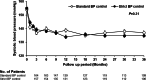
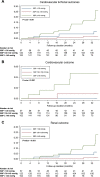
Results: A total of 341 participants were included in the analysis. Over a median follow-up of 2.8 years, cardiovascular/renal events were observed in 25 (7.3%) participants. Mean (SD) SBPs in the standard and strict BP control group were 140.2 (11.6) and 140.2 (11.9) mmHg, respectively. The strict BP control group did not show significantly reduced risk of cardiovascular/renal events (HR 1.32; 95% CI 0.60-2.92]). In the post-hoc analyses using achieved BP, achieved average SBP of 130-139 mmHg resulted in reduced risk of cardiovascular/renal events (HR 0.15; 95% CI 0.03-0.67) compared to achieved average SBP ≥ 140 mmHg, whereas further reduction in achieved average SBP < 130 mmHg did not impart additional benefits.
Conclusion: In patients with DKD, targeting a SBP of less than 130 mmHg, as compared with less than 140 mmHg, did not reduce the rate of a composite of cardiovascular and renal events. Achieved SBP of 130-139 mmHg was associated with a decreased risk for the primary outcome in patients with DKD.
Trial registration: ClinicalTirals.gov Identifier: NCT02620306, registered December 3, 2015. ( https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02620306 ).
Keywords: Blood pressure; Cardiovascular outcome; Diabetic kidney disease; Kidney outcome.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.P. received lecture fees from Boryoung, Hanmi, Daewoong, Donga, Celltrion, Servier, Daiichi Sankyo and Daewon. S.P. also received research grant from Daiichi Sankyo. Y.J.K. received consultation fee from Celltrion and received lecture fees from Yuhan, Daewoong, Daiichi Sankyo, Bayer, Takeda, and GC pharma. S.J.H. received lecture fees and research sponsoring from Hanmi, InnoN, Samjin and Boryung. S.G.K. received lecture fees and research sponsoring from Yuhan, JW Pharma, AstraZeneca, GSK, Fibrogen, Akebia, Omeros, Chinook, MorphoSys, Otsuka and Boryung. J.C.W. received lecture fees and research sponsoring from Chong Kun Dang, Daewoong, Eli Lilly, Yuhan and Boryung.
Figures
References
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Blood Pressure Working Group. KDIGO 2021 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Blood Pressure in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2021;99(3S):S1–87. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
