Xylazine is an agonist at kappa opioid receptors and exhibits sex-specific responses to opioid antagonism
- PMID: 39086495
- PMCID: PMC11290297
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addicn.2024.100155
Xylazine is an agonist at kappa opioid receptors and exhibits sex-specific responses to opioid antagonism
Abstract
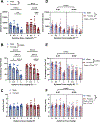
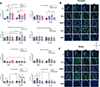
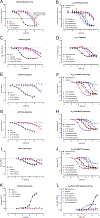
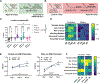
Xylazine is in the unregulated drug supply at increasing rates, usually combined with fentanyl, necessitating understanding of its pharmacology. Despite commentary from politicians, and public health officials, it is unknown how xylazine impacts naloxone efficacy, and. few studies have examined it alone. Here, we examine the impact of xylazine alone and in combination with fentanyl on several behaviors in mice. Surprisingly, naloxone precipitates withdrawal from xylazine and fentanyl/xylazine coadministration, with enhanced sensitivity in females. Further, xylazine is a full agonist at kappa opioid receptors, a potential mechanism for its naloxone sensitivity. Finally, we demonstrate surprising effects of xylazine to kappa opioid antagonism, which are relevant for public health considerations. These data address an ongoing health crisis and will help inform critical policy and healthcare decisions.
Keywords: Fentanyl; Mouse; Opioid; Pharmacology; Xylazine.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest MLB, ACN, and ZAM are subcontracted by Epicypher® on an unrelated project. ND is an uncompensated board member of Remedy Alliance For The People, a 501(c)3 non-profit organization that distributes naloxone. BRL is on the SAB of several companies: Septerna, Onsero, Epiodyne, Escient; he has stock in Septerna; and he has had many technologies licensed by UNC to pharmaceutical and biotech companies. The remaining authors do not have any disclosures.
Figures

References
-
- Elejalde JI, Louis CJ, Elcuaz R, Pinillos MA, Drug abuse with inhalated xylazine, Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 10 (2003) 252–253, 10/brfztn. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann U, Meister CM, Golle K, Zschiesche M, Severe intoxication with the veterinary tranquilizer xylazine in humans, J. Anal. Toxicol. 25 (2001) 245–249, 10/gsk7kz. - PubMed
-
- Spoerke DG, Hall AH, Grimes MJ, Honea BN, Rumack BH, Human overdose with the veterinary tranquilizer xylazine, Am. J. Emerg. Med. 4 (1986) 222–224, 10/bm5b8h. - PubMed
-
- Gallanosa AG, Spyker DA, Shipe JR, Morris DL, Human xylazine overdose: a comparative review with clonidine, phenothiazines, and tricyclic antidepressants, Clin. Toxicol. 18 (1981) 663–678, 10/bbt8mn. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
