DOX-PLGA Nanoparticles Effectively Suppressed the Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines TNF-a, IL-6, iNOS, and IL-1β in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Line
- PMID: 39086585
- PMCID: PMC11288233
- DOI: 10.61186/rbmb.12.4.530
DOX-PLGA Nanoparticles Effectively Suppressed the Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines TNF-a, IL-6, iNOS, and IL-1β in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Line
Abstract
Background: Inflammation contributes to cancer pathobiology through different mechanisms. Higher levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines can lead to hyperinflammation and promote cancer development and metastasis. For cancer treatment, Doxorubicin (DOX) can be encapsulated into the poly-lactic-glycolic acid (PLGA) nanoparticles. This study aimed to investigate the impact of doxorubicin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles (DOX-PLGA NP) on the expression of pro-inflammatory genes TNF-α, IL-6, iNOS, and IL-1β in the MCF-7 cells.
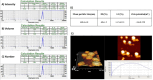
Methods: The DOX-PLGA NP was prepared by loading doxorubicin into PLGA and characterized using dynamic light scattering (DLS) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). The cytotoxic effect of the nanoparticles was determined by the MTT assay, and their impacts on the expression of pro-inflammatory genes were assessed by qRT-PCR.
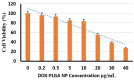
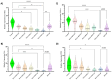
Results: The encapsulation efficiency and loading capacity were 60±1.5 and 1.13±0.21 percent, respectively. The zeta potential and mean DOX-PLGA nanoparticle size were -18±0.550 mV and 172±55.6 nm, respectively. The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of the DOX-PLGA NP on MCF-7 cell viability was 24.55 µg/mL after 72 hours of treatment. The qRT-PCR results revealed that the 20 µg/mL concentration of the DOX-PLGA NP significantly suppressed the expression of the pro-inflammatory genes TNF-α, IL-6, iNOS, and IL-1β compared to DOX alone (20 µg/mL). Additionally, the suppression effect of DOX-PLGA NP on the expression of these pro-inflammatory genes was dose-dependent.
Conclusions: These results show that DOX-PLGA NP efficiently suppressed the expression of pro-inflammatory genes. Furthermore, encapsulation of DOX into PLGA nanoparticles significantly improved the effectiveness of DOX in suppressing pro-inflammatory genes in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Cytokines; Doxorubicin; Polylactic Acid-Polyglycolic Acid Copolymer; Pro-inflammatory cytokine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
5-Fluorouracil-Loaded PLGA Declined Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Genes IL-9, IL-17A, IL-23 and IFN- y; in the HT-29 Colon Cancer Cell Line.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2024 Jan;12(4):664-673. doi: 10.61186/rbmb.12.4.664. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39086581 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan-Dextran sulfate coated doxorubicin loaded PLGA-PVA-nanoparticles caused apoptosis in doxorubicin resistance breast cancer cells through induction of DNA damage.Sci Rep. 2017 May 19;7(1):2143. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02134-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28526868 Free PMC article.
-
Co-culture system of breast cancer and normal cells to investigate inflammation: using doxorubicin encapsulated in adipose-derived exosomes.Med Oncol. 2024 Dec 4;42(1):21. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02568-2. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39630192
-
Combination nanochemotherapy of brain tumor using polymeric nanoparticles loaded with doxorubicin and paclitaxel: An in vitro and in vivo study.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2023 Dec;193:175-186. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2023.11.002. Epub 2023 Nov 4. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2023. PMID: 37926270
-
Development and optimization of doxorubicin loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanobubbles for drug delivery into HeLa cells.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014 Apr;14(4):2947-54. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2014.8633. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24734715
Cited by
-
Algae-Mediated Green Synthesis of Dextran-Coated Titanium Nanoparticles and Their Cytotoxic Potential Against MCF7 Breast Cancer Cells.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2024 Oct;13(3):358-367. doi: 10.61186/rbmb.13.3.358. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 40330561 Free PMC article.
-
5-Fluorouracil-Loaded PLGA Declined Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Genes IL-9, IL-17A, IL-23 and IFN- y; in the HT-29 Colon Cancer Cell Line.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2024 Jan;12(4):664-673. doi: 10.61186/rbmb.12.4.664. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39086581 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Helicobacter Pylori-Derived Outer Membrane Vesicles on Inflammation, Immune Responses, and Tumor Cell Migration in Breast Cancer Through the Snail/Β-Catenin Pathway.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2024 Jul;13(2):263-272. doi: 10.61186/rbmb.13.2.263. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39995644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. The Global Breast Cancer Initiative. 2023 February 3; Available from: https://www.who.int/initiatives/global-breast-cancer-initiative.htm.
-
- Budny A, Starosławska E, Budny B. Epidemiologia oraz diagnostyka raka piersi. Pol Merkuriusz Lek. 2019;46(275):195–204. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
