The Potential Association Between microRNA 135-5P and p62 and Their Effect on NRF2 Pathway in Multiple Sclerosis
- PMID: 39086595
- PMCID: PMC11288234
- DOI: 10.61186/rbmb.12.4.512
The Potential Association Between microRNA 135-5P and p62 and Their Effect on NRF2 Pathway in Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
Background: Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a prevalent non-traumatic disabling disease affecting young adults, characterized by complexity in its pathogenesis. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 (NRF2) serves as a crucial transcriptional regulator of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant enzymes, influenced by the ubiquitous protein p62. It acts as a scaffold directing substrates to autophagosomes. This study aims to explore the potential association between microRNA 135-5p and p62 and their impact on inflammation and oxidative stress through the NRF2 pathway in MS.
Methods: The study included 30 healthy controls and 60 MS patients (relapsing-remitting and secondary progressive). Real-time PCR was employed for the detection of Nrf2, p62, miRNA135-5P, and NF-κB in serum, while p53 levels were determined using ELISA.
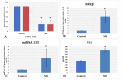
Results: Nrf2 and p62 expression was significantly downregulated in the MS group compared to controls. Conversely, miRNA135-5P, NF-κB expression, and P53 levels were significantly elevated in the MS group.
Conclusions: This study reveals a potential association between miRNA 135-5p and p62, indicating their role in the pathogenesis of MS. Results suggest that miRNA 135-5p and p62 may influence inflammation and oxidative stress in MS through the NRF2 pathway, potentially mediated by NF-κB and p53.
Keywords: Microrna135; Multiple sclerosis; NRF2; p62.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nellessen A, Nyamoya S, Zendedel A, Slowik A, Wruck C, Beyer C, et al. Nrf2 deficiency increases oligodendrocyte loss, demyelination, neuroinflammation and axonal damage in an MS animal model. Metab Brain Dis. 2020;35(2):353–362. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
