An Analytical Model of NPS and DQE Comparing Photon Counting and Energy Integrating Detectors
- PMID: 39086656
- PMCID: PMC11290553
- DOI: 10.1117/12.845310
An Analytical Model of NPS and DQE Comparing Photon Counting and Energy Integrating Detectors
Abstract
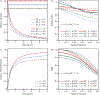
In this work, analytical models of the optical transfer function (OTF), noise power spectra (NPS), and detective quantum efficiency (DQE) are developed for two types of digital x-ray detectors. The two detector types are (1) energy integrating (EI), for which the point spread function (PSF) is interpreted as a weighting function for counting x-rays, and (2) photon counting (PC), for which the PSF is treated as a probability. The OTF is the Fourier transform of the PSF. The two detector types, having the same PSF, possess an equivalent OTF. NPS is the discrete space Fourier transform (DSFT) of the autocovariance of signal intensity. From first principles, it is shown that while covariance is equivalent for both detector types, variance is not. As a consequence, provided the two detector types have equivalent PSFs, a difference in NPS exists such that NPSPC ≥ NPSEI and hence DQEPC ≤ DQEEI. The necessary and sufficient condition for equality is that the PSF is either zero or unity everywhere. A PSF modeled as the convolution of a Lorentzian with a rect function is analyzed in order to illustrate the differences in NPS and DQE. The Lorentzian models the blurring of the x-ray converter, while the rect function reflects the sampling of the detector. The NPS difference between the two detector types is shown to increase with increasing PSF width. In conclusion, this work develops analytical models of OTF, NPS, and DQE for energy integrating and photon counting digital x-ray detectors.
Keywords: Energy integrating detector; detective quantum efficiency (DQE); modulation transfer function (MTF); noise power spectra (NPS); optical transfer function (OTF); photon counting detector; point spread function (PSF).
Figures


References
-
- Samei E, “Image quality in two phosphor-based flat panel digital radiographic detectors,” Med. Phys 30(7), 1747–1757 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Rowlands JA and Yorkston J, in Handbook of Medical Imaging, edited by Beutel J, Kundel HL, and van Metter RL (SPIE, Bellingham, WA, 2000), Vol. 1, Chap. 4.
-
- Jing T, Goodman CA, Drewery J, Cho G, Hong WS, Lee H, Kaplan SN, Mireshghi A, Perez-Mendez V, and Wildermuth D, “Amorphous silicon pixel layers with cesium iodide converters for medical radiography,” IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci 41(4), 903–909 (1994).
-
- Cowen A, Kengyelics S, and Davies A, “Solid-state, flat-panel, digital radiography detectors and their physical imaging characteristics,” Clin. Radiol 63(5), 487–498 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Nagarkar VV, Gupta TK, Miller SR, Klugerman Y, Squillante MR, and Entine G, “Structured CsI(Tl) scintillators for x-ray imaging applications,” IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci 45(3), 492–496 (1998).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
