Recovery from social isolation requires dopamine in males, but not the autism-related gene nlg3 in either sex
- PMID: 39086833
- PMCID: PMC11288677
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.240604
Recovery from social isolation requires dopamine in males, but not the autism-related gene nlg3 in either sex
Abstract
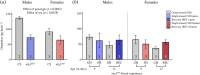
Social isolation causes profound changes in social behaviour in a variety of species. However, the genetic and molecular mechanisms modulating behavioural responses to social isolation and social recovery remain to be elucidated. Here, we quantified the behavioural response of vinegar flies to social isolation using two distinct protocols (social space preference and sociability, the spontaneous tendencies to form groups). We found that social isolation increased social space and reduced sociability. These effects of social isolation were reversible and could be reduced after 3 days of group housing. Flies with a loss of function of neuroligin3 (orthologue of autism-related neuroligin genes) with known increased social space in a socially enriched environment were still able to recover from social isolation. We also show that dopamine (DA) is needed for a response to social isolation and recovery in males but not in females. Furthermore, only in males, DA levels are reduced after isolation and are not recovered after group housing. Finally, in socially enriched flies mutant for neuroligin3, DA levels are reduced in males, but not in females. We propose a model to explain how DA and neuroligin3 are involved in the behavioural response to social isolation and its recovery in a dynamic and sex-specific manner.
Keywords: dopamine; neuroligin; recovery; social behaviour; social isolation; social space.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Rubenstein DR, Hofmann HA. 2015. Proximate pathways underlying social behavior. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 6 , 154–159. ( 10.1016/j.cobeha.2015.11.007) - DOI
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
