ANA-associated arthritis: clinical and biomarker characterization of a population for basket trials
- PMID: 39087598
- PMCID: PMC11534109
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae269
ANA-associated arthritis: clinical and biomarker characterization of a population for basket trials
Abstract
Objectives: ANA-associated rheumatic and musculoskeletal (MSK) diseases (RMDs) [SLE, primary SS (pSS), scleroderma, inflammatory myositis, MCTD and UCTD] make up a disease spectrum with overlapping clinical and immunological features. MSK inflammation is common and impactful across ANA-associated RMDs. The objectives of this study were to evaluate MSK inflammation (ANA-associated arthritis) prevalence in a multidisease ANA-associated RMD study, assess its clinical impact across ANA-associated RMD diagnoses, propose new basket groupings of patients, and evaluate immunological profiles in legacy and new basket contexts.
Methods: An observational study enrolled patients with ANA-associated RMDs. Demographic variables, comorbidities, therapies, disease activity instruments [BILAG, SLEDAI, the EULAR SS disease activity index (ESSDAI), physician visual analogue scale (VAS)], patient-reported outcomes [SF36, FACIT-Fatigue, EQ5D, ICECAP-A, Work Productivity and Activity impairment (WPAI), patient VAS] and the biomarker profile (six-gene expression scores, flow cytometry, autoantibody profile) were analysed. Reclustering utilized Gaussian mixture modelling (GMM). The clinical and immune features of new and legacy clusters were compared.
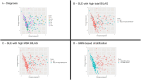
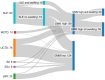
Results: Inflammatory MSK symptoms were prevalent across ANA-associated RMDs, in 213/294 patients. In ANA-associated arthritis patients, most variables did not differ between diagnoses, with the exception of the EQ5D-5L index and mobility domains (lower in MCTD/pSS, both P < 0.05). FM and OA prevalence were similar across diagnoses. Therapy use differed significantly, the use of biologics being greatest in SLE (P < 0.05). GMM yielded two multidisease clusters: High MSK disease activity (n = 89) and low MSK disease activity (n = 124). The high MSK disease activity cluster included all patients with active joint swelling, and they had significantly higher prednisolone usage, physician global assessment (PGA), Sm/RNP/SmRNP/chromatin positivity, Tetherin mean fluorescence intensity (MFI), and IFN Score-A activity, along with numerically lower FM and OA prevalence.
Conclusion: We defined ANA-associated arthritis, a more clinically and immunologically homogeneous population than existing RMD populations for trials, and a more prevalent population for therapies in the clinic.
Keywords: SLE; Sjögren’s syndrome; arthritis; autoimmune diseases; myositis.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures



References
-
- Mosca M, Tani C, Vagnani S, Carli L, Bombardieri S. The diagnosis and classification of undifferentiated connective tissue diseases. J Autoimmun 2014;48-49:50–2. - PubMed
-
- Mosca M, Tani C, Neri C et al. Analysis of the evolution to defined connective tissue diseases of patients with “early unidifferentiated connective tissue diseases (UCTD.).” Reumatismo 2008;60:35–40. - PubMed
-
- Ceccarelli F, Perricone C, Cipriano E et al. Joint involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus: from pathogenesis to clinical assessment. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2017;47:53–64. - PubMed
-
- Fauchais A-L, Ouattara B, Gondran G et al. Articular manifestations in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: clinical significance and prognosis of 188 patients. Rheumatology 2010;49:1164–72. - PubMed

