Kv7 channel opener retigabine reduces self-administration of cocaine but not sucrose in rats
- PMID: 39087789
- PMCID: PMC11292668
- DOI: 10.1111/adb.13428
Kv7 channel opener retigabine reduces self-administration of cocaine but not sucrose in rats
Abstract
The increasing rates of drug misuse highlight the urgency of identifying improved therapeutics for treatment. Most drug-seeking behaviours that can be modelled in rodents utilize the repeated intravenous self-administration (SA) of drugs. Recent studies examining the mesolimbic pathway suggest that Kv7/KCNQ channels may contribute to the transition from recreational to chronic drug use. However, to date, all such studies used noncontingent, experimenter-delivered drug model systems, and the extent to which this effect generalizes to rats trained to self-administer drugs is not known. Here, we tested the ability of retigabine (ezogabine), a Kv7 channel opener, to regulate instrumental behaviour in male Sprague Dawley rats. We first validated the ability of retigabine to target experimenter-delivered cocaine in a conditioned place preference (CPP) assay and found that retigabine reduced the acquisition of place preference. Next, we trained rats for cocaine-SA under a fixed-ratio or progressive-ratio reinforcement schedule and found that retigabine pretreatment attenuated the SA of low to moderate doses of cocaine. This was not observed in parallel experiments, with rats self-administering sucrose, a natural reward. Compared with sucrose-SA, cocaine-SA was associated with reductions in the expression of the Kv7.5 subunit in the nucleus accumbens, without alterations in Kv7.2 and Kv7.3. Therefore, these studies reveal a reward-specific reduction in SA behaviour and support the notion that Kv7 is a potential therapeutic target for human psychiatric diseases with dysfunctional reward circuitry.
Keywords: Kv7 channel; cocaine self‐administration; retigabine.
© 2024 The Author(s). Addiction Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society for the Study of Addiction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


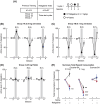
 7 mg/kg). Significance compared with saline at the cocaine unit doses of 0.5 mg (7 mg/kg, **p = 0.0133) and 0.1 mg (2 mg/kg, **p = 0.0027; 5 and 7 mg/kg, ****p < 0.0001) using a Šídák's multiple comparison test.
7 mg/kg). Significance compared with saline at the cocaine unit doses of 0.5 mg (7 mg/kg, **p = 0.0133) and 0.1 mg (2 mg/kg, **p = 0.0027; 5 and 7 mg/kg, ****p < 0.0001) using a Šídák's multiple comparison test.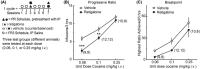
Update of
-
K v 7 Channel Opener Retigabine Reduces Self-Administration of Cocaine but Not Sucrose in Rats.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 22:2023.05.18.541208. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.18.541208. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Addict Biol. 2024 Aug;29(8):e13428. doi: 10.1111/adb.13428. PMID: 37292619 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

