Modeling late-onset Alzheimer's disease neuropathology via direct neuronal reprogramming
- PMID: 39088624
- PMCID: PMC11787906
- DOI: 10.1126/science.adl2992
Modeling late-onset Alzheimer's disease neuropathology via direct neuronal reprogramming
Abstract
Late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD) is the most common form of Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, modeling sporadic LOAD that endogenously captures hallmark neuronal pathologies such as amyloid-β (Aβ) deposition, tau tangles, and neuronal loss remains an unmet need. We demonstrate that neurons generated by microRNA (miRNA)-based direct reprogramming of fibroblasts from individuals affected by autosomal dominant AD (ADAD) and LOAD in a three-dimensional environment effectively recapitulate key neuropathological features of AD. Reprogrammed LOAD neurons exhibit Aβ-dependent neurodegeneration, and treatment with β- or γ-secretase inhibitors before (but not subsequent to) Aβ deposit formation mitigated neuronal death. Moreover inhibiting age-associated retrotransposable elements in LOAD neurons reduced both Aβ deposition and neurodegeneration. Our study underscores the efficacy of modeling late-onset neuropathology of LOAD through high-efficiency miRNA-based neuronal reprogramming.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

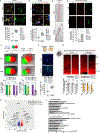
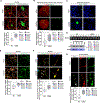
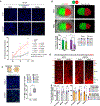
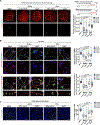
Update of
-
Endogenous recapitulation of Alzheimer's disease neuropathology through human 3D direct neuronal reprogramming.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 25:2023.05.24.542155. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.24.542155. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Science. 2024 Aug 2;385(6708):adl2992. doi: 10.1126/science.adl2992. PMID: 37292658 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Alzheimer A, Stelzmann RA, Schnitzlein HN, Murtagh FR, An English translation of Alzheimer’s 1907 paper, “Uber eine eigenartige Erkankung der Hirnrinde”. Clin Anat 8, 429–431 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Zetterberg H, Mattsson N, Understanding the cause of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Rev Neurother 14, 621–630 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

