2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Management in Korea: Full Version Recommendation of the Korean Diabetes Association
- PMID: 39091005
- PMCID: PMC11307112
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0249
2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Management in Korea: Full Version Recommendation of the Korean Diabetes Association
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
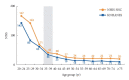
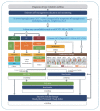
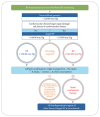
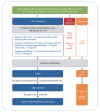
Figures
References
-
- Oh JY, Lim S, Kim DJ, Kim NH, Kim DJ, Moon SD, et al. The diagnosis of diabetes mellitus in Korea: a pooled analysis of four community-based cohort studies. Diabet Med. 2007;24:217–8. - PubMed
-
- Oh JY, Lim S, Kim DJ, Kim NH, Kim DJ, Moon SD, et al. A report on the diagnosis of intermediate hyperglycemia in Korea: a pooled analysis of four community-based cohort studies. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008;80:463–8. - PubMed
-
- International Diabetes Federation Clinical Guidelines Task Force . Global guideline for type 2 diabetes. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2005.
-
- World Health Organization Regional Office for the Western Pacific . Type 2 diabetes: practical targets and treatments. 4th ed. Melbourne: International Diabetes Institute; 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

