Loganin Ameliorates Acute Kidney Injury and Restores Tofacitinib Metabolism in Rats: Implications for Renal Protection and Drug Interaction
- PMID: 39091013
- PMCID: PMC11392661
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2024.008
Loganin Ameliorates Acute Kidney Injury and Restores Tofacitinib Metabolism in Rats: Implications for Renal Protection and Drug Interaction
Abstract
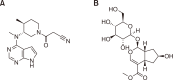
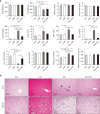
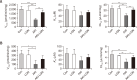
Tofacitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, is metabolized through hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP), specifically CYP3A1/2 and CYP2C11. Prolonged administration of rheumatoid arthritis medications is generally associated with an increased risk of renal toxicity. Loganin (LGN), an iridoid glycoside, has hepatorenal regenerative properties. This study investigates the potential of LGN to mitigate acute kidney injury (AKI) and its effects on the pharmacokinetics of tofacitinib in rats with cisplatin-induced AKI. Both intravenous and oral administration of tofacitinib to AKI rats significantly increased the area under the plasma concentration-time curve from time 0 to infinity (AUC) compared with control (CON) rats, an increase attributed to the decelerated non-renal clearance (CLNR) and renal clearance (CLR) of tofacitinib. Administration of LGN to AKI rats, however, protected kidneys from severe impairment, restoring the pharmacokinetic parameters (AUC, CLNR, and CLR) of tofacitinib to those observed in untreated CON rats, with partial recovery of kidney function, as evidenced by an increase in creatinine clearance (CLCR). Possible interactions between drugs and natural components should be considered, especially when co-administering both a drug and a natural extract containing LGN or iridoid glycosides to patients with kidney injury.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; CYP2C11; CYP3A1/2; Loganin; Pharmacokinetics; Tofacitinib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
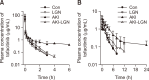

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

