Tetanus-diphtheria vaccine can prime SARS-CoV-2 cross-reactive T cells
- PMID: 39091504
- PMCID: PMC11291333
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425374
Tetanus-diphtheria vaccine can prime SARS-CoV-2 cross-reactive T cells
Abstract
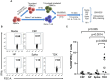
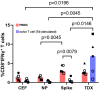
Vaccines containing tetanus-diphtheria antigens have been postulated to induce cross-reactive immunity to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which could protect against coronavirus disease (COVID-19). In this work, we investigated the capacity of Tetanus-diphtheria (Td) vaccine to prime existing T cell immunity to SARS-CoV-2. To that end, we first collected known SARS-CoV-2 specific CD8+ T cell epitopes targeted during the course of SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans and identified as potentially cross-reactive with Td vaccine those sharing similarity with tetanus-diphtheria vaccine antigens, as judged by Levenshtein edit distances (≤ 20% edits per epitope sequence). As a result, we selected 25 potentially cross-reactive SARS-CoV-2 specific CD8+ T cell epitopes with high population coverage that were assembled into a synthetic peptide pool (TDX pool). Using peripheral blood mononuclear cells, we first determined by intracellular IFNγ staining assays existing CD8+ T cell recall responses to the TDX pool and to other peptide pools, including overlapping peptide pools covering SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein and Nucleocapsid phosphoprotein (NP). In the studied subjects, CD8+ T cell recall responses to Spike and TDX peptide pools were dominant and comparable, while recall responses to NP peptide pool were less frequent and weaker. Subsequently, we studied responses to the same peptides using antigen-inexperienced naive T cells primed/stimulated in vitro with Td vaccine. Priming stimulations were carried out by co-culturing naive T cells with autologous irradiated peripheral mononuclear cells in the presence of Td vaccine, IL-2, IL-7 and IL-15. Interestingly, naive CD8+ T cells stimulated/primed with Td vaccine responded strongly and specifically to the TDX pool, not to other SARS-CoV-2 peptide pools. Finally, we show that Td-immunization of C57BL/6J mice elicited T cells cross-reactive with the TDX pool. Collectively, our findings support that tetanus-diphtheria vaccines can prime SARS-CoV-2 cross-reactive T cells and likely contribute to shape the T cell responses to the virus.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; T cell cross-reactivity; epitope; tetanus-diphtheria toxoid vaccines.
Copyright © 2024 Fernandez, Pelaez-Prestel, Fiyouzi, Gomez-Perosanz, Reiné and Reche.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Potential Cross-Reactive Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 From Common Human Pathogens and Vaccines.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 16;11:586984. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.586984. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33178220 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical evaluation of a synthetic peptide vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 inducing multiepitopic and cross-reactive humoral neutralizing and cellular CD4 and CD8 responses.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021 Dec;10(1):1931-1946. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1978823. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021. PMID: 34538222 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid and Spike T-Cell Epitopes for Assessing T-Cell Immunity.J Virol. 2021 Feb 24;95(6):e02002-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02002-20. Print 2021 Feb 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33443088 Free PMC article.
-
Degenerate CD8 Epitopes Mapping to Structurally Constrained Regions of the Spike Protein: A T Cell-Based Way-Out From the SARS-CoV-2 Variants Storm.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 8;12:730051. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.730051. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34566990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of multi-epitope peptide-based vaccines against SARS-CoV-2.Biomed J. 2021 Mar;44(1):18-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.09.005. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Biomed J. 2021. PMID: 33727051 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for determining neutrophil elastase (NE) - a potential useful marker of multi-organ damage observed in COVID-19 and post-Covid-19 (PCS).Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Feb 25;12:1542898. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1542898. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40070691 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

