Characterization of the in vitro metabolic profile of nazartinib in HLMs using UPLC-MS/MS method: In silico metabolic lability and DEREK structural alerts screening using StarDrop software
- PMID: 39091946
- PMCID: PMC11292529
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34109
Characterization of the in vitro metabolic profile of nazartinib in HLMs using UPLC-MS/MS method: In silico metabolic lability and DEREK structural alerts screening using StarDrop software
Abstract
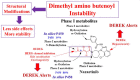
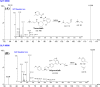
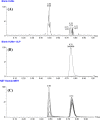
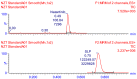
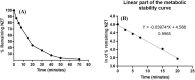
The orally given, irreversible, third-generation inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), known as Nazartinib (EGF816), is now undergoing investigation in Phase II clinical trials conducted by Novartis for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. The primary aim of the current research was to establish a rapid, specific, environmentally friendly, and highly versatile UPLC-MS/MS methodology for the determination of nazartinib (NZT) levels in human liver microsomes (HLMs). Subsequently, same approach was used to examine the metabolic stability of NZT. The UPLC-MS/MS method employed in HLMs was validated as stated in the bioanalytical method validation criteria outlined by the US- FDA. The evaluation of the metabolic stability of NZT and the identification of potentially structural alarms were performed using the StarDrop software package that includes the P450 and DEREK software. The calibration curve for NZT showed a linearity in the range from 1 to 3000 ng/mL. The inter-day accuracy and precision exhibited a range of values between -4.33 % and 4.43 %, whereas the intra-day accuracy and precision shown a range of values between -2.78 % and 7.10 %. The sensitivity of the developed approach was verified through the determination of a LLOQ of 0.39 ng/mL. The intrinsic clearance and in vitro half-life of NZT were assessed to be 46.48 mL/min/kg and 17.44 min, respectively. In our preceding inquiry, we have effectively discerned the bioactivation center, denoted by the carbon atom between the unsaturated conjugated system and aliphatic linear tertiary amine. In the context of computational software, making minor adjustments or substituting the dimethylamino-butenoyl moiety throughout the drug design process may increase the metabolic stability and safety properties of new synthesized derivatives. The efficiency of utilizing different in silico software approaches to conserve resources and reduce effort was proved by the outcomes attained from in vitro incubation experiments and the use of NZT in silico software.
Keywords: DEREK program; Greenness; Metabolic stability; Nazartinib; StarDrop software; UPLC-MS/MS.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Bray F., et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Barinaga M. From bench top to bedside. Science. 1997;278(5340):1036–1039. - PubMed
-
- Shenouda S.K., Alahari S.K. MicroRNA function in cancer: oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009;28(3–4):369. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

